I update this from time to time to keep track of walks I have done and to keep them on the internet in case anyone is searching for someone to give a walk on one of ‘my’ subjects.
The ‘London Before and After the Roman invasion Walk’ was a brand new walk, although I had done it as a virtual tour.. But as an actual walk it was new and quite a challenge. Although the Roman finds are concentrated in an area that can reasonably be ‘walked’ the prehistoric element is spread all over Greater London. So I did quite a lot of waving my arms and saying ‘Over there, archaeologists found….’ or ‘To the South East was the Kingdom of the Atrebates, whose King Verica fled to the Romans asking their help to regain his throne. ‘ or ‘Claudius crossed the Thames with Nine Elephants some where, almost certainly to the West of us.’ It went quite well, although the sunny weather changed into a downpour which made the climax of the tour a bit of a damp squib.
But I learnt a lot, because it made me read Dominic Perring’s new book on Roman London ‘London in the Roman World’ more closely than I otherwise would have. I should say that I worked with Dominic when we were young archaeologists at the Museum of London. He is now a Professor at the Institute of Archaeology, and, occasionally, I am lucky enough to join him and a few archaeological friends, watching our football team, Tottenham Hotspur.
Tomorrow is my Plough Tuesday as I spent today, my last day of my ‘holiday’ period, bringing my boat up the Regent’s Canal to outside my flat in Hackney and what a glorious January day it was! Tomorrow I have a meeting to sort out my Road Scholar lecturing for the year and Wednesday is my first day lecturing at College.
Below are the walks I have done so far this year
Ring in the New Year Virtual Walk

Monday 1st January 2024 7.00pm
On this Virtual Walk we look at how London has celebrated the New Year over the past 2000 years.
The New Year has been a time of review, renewal and anticipation
of the future from time immemorial. The Ancient Britons saw the Solstice as a symbol of a promise of renewal as the Sun was reborn. As the weather turns to bleak mid winter, a festival or reflection and renewal cheers everyone up. This idea of renewal was followed by the Romans, and presided over by a two headed God called Janus who looked both backwards and forwards. Dickens Christmas Carol was based on redemption and his second great Christmas Book ‘The Chimes’ on the renewal that the New Year encouraged.
We look at London’s past to see where and how the New Year was celebrated. We also explore the different New Years we use and their associated Calendars – the Pagan year, the Christian year, the Roman year, the Jewish year, the Financial year, the Academic year and we reveal how these began. We look at folk traditions, Medieval Christmas Festivals, Boy Bishops, Distaff Sunday and Plough Monday, and other Winter Festival and New Year London tradition and folklore.
At the end we use ancient methods to divine what is in store for us in 2023..
The virtual walk finds interesting and historic places in the City of London to link to our stories of Past New Year’s Days. We begin with the Druids at Tower Hill, and walk around the Roman City of London, and through London History until we get to St Pauls Cathedral
The London Winter Solstice Virtual Tour
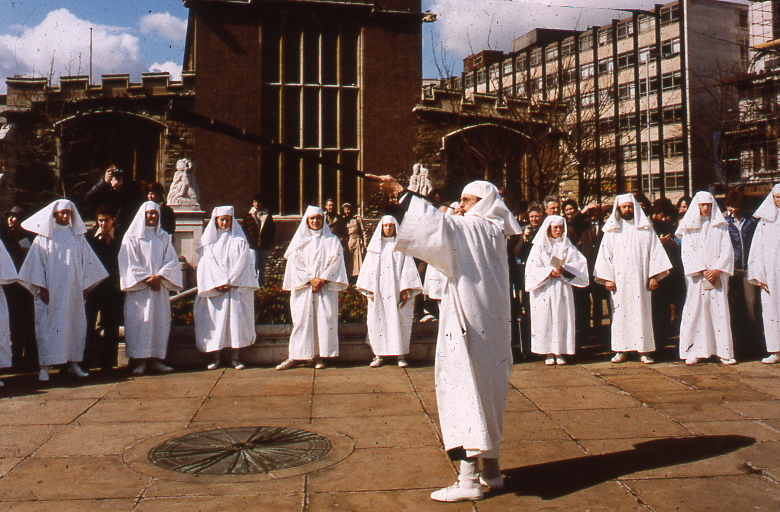

Fri 22 Dec 2023 19:30
We explore London’s History through its celebrations, festivals, calendars and almanacs of the Winter Solstice
Winter Solstice festivals have been a time of review, renewal and anticipation of the future from time immemorial. The Ancient Britons saw the Solstice as a symbol of a promise of renewal as the world entered bleak mid winter. The Roman season was presided over by Janus, a two headed God who looked both backwards and forwards, and Dickens based his second great Christmas Book on the renewal that the New Year encouraged.
We look at London’s past to see where and how the Solstice might be celebrated. We also explore the different Calendars – the Pagan year, the Christian year, the Roman year, the Jewish year, the Financial year, the Academic year and we reveal how these began. We look at folk traditions, Medieval Christmas Festivals, Boy Bishops, Distaff Sunday and Plough Monday, and other London winter traditions and folklore.
At the end we use ancient methods to divine what is in store for us in 2023.
To Book:
Jane Austen’s London Walk

Jane Austen’s London Walk
a Special Christmas version on 23 December 2023 & normal one on 21st January
Sat 2.30 pm Green Park underground station, London (By the Fountain, just outside the Green Park exit of the Tube Station)
To Book:
An exploration of Mayfair, the centre of the London section of Sense & Sensibility and where Jane came to visit her brother
“It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a Jane Austen devotee in possession of the good fortune of a couple of free hours today must be in want of this walk.”
People associate Jane Austen and her characters with a rural setting. But London is central to both Jane Austen’s real life and her literary life. So, this tour will explore Jane’s connections with London and give the background to Sense and Sensibility, a good part of which is based in this very area. We begin with the place Jane’s coach would arrive from Hampshire, and then walk the streets haunted by Willougby; past shops visited by the Palmers, the Ferrars; visit the location of Jane Austen’s brother’s bank and see the publisher of Jane’s Books. The area around Old Bond Street was the home of the Regency elite and many buildings and a surprising number of the shops remain as they were in Jane Austen’s day.
This is a London Walk Guided Walk lead by Kevin Flude
To Book:
Christmas With Jane Austen Virtual London Tour

Saturday 23 December 2023 7.30pm
We look at how Jane Austen spent Christmas and at Georgian Christmas traditions and amusements.
“It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a Jane Austen devotee in possession of the good fortune of a couple of free hours must be in want of this virtual walk.”
This is a special walk, which looks at the traditions of Christmas during the Regency period and how Jane Austen might have celebrated it. It will give some background to Jane Austen’s life and her knowledge of London. We used her novels and her letters to find out what she might have done at Christmas, but also at how Christmas was kept in this period, and the range of ‘Curiosities, Amusements, Exhibitions, Public Establishments, and Remarkable Objects in and near London available to enjoy.
This is a London Walks Guided Walk by Kevin Flude, Museum Curator and Lecturer.
Review: ‘Thanks, again, Kevin. These talks are magnificent!’
To Book:
Roman London – A Literary & Archaeological Walk Saturday 16 Dec & 21st Jan 2023 11.30 am Monument Underground Station To book
Dickens London. Life, Work and Christmas Virtual Tour

Friday 15th December 2023 7.30pm
A Virtual Tour of Dickens London with a dash of Dickensian Christmas
The Virtual Tour weaves an exploration of Victorian London with Dickens London Life and writing. On the tour we have a look at London at Christmas and the contribution Dickens made to it by his Christmas Books
Dickens writing always has a moral element as exemplified by his Christmas Books. ‘Christmas Carol’ was based on redemption and his second great Christmas Book ‘The Chimes’ on the renewal that the New Year encouraged.
We start in Southwark, visit sites associated with the Christmas Books and others and end at Staple Inn with the Christmas Book ‘The Haunted Man’.
Chaucer’s Medieval London Guided Walk
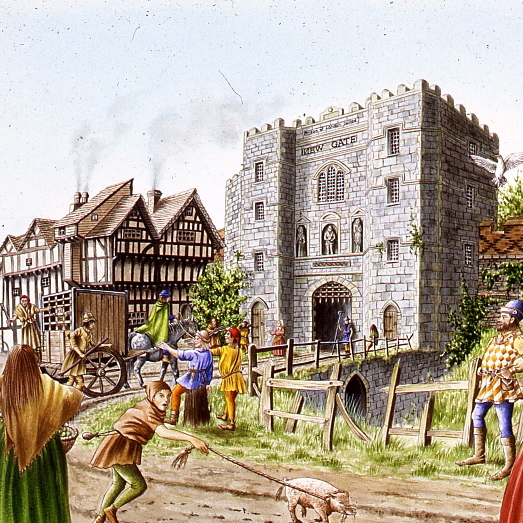

Aldgate Underground Sunday 12 November 2023 11.30pm
A Walk around Medieval London following in the footsteps of its resident medieval poet – Geoffrey Chaucer
One of the spectators at the Peasants Revolt was Geoffrey Chaucer, born in the Vintry area of London, who rose to be a diplomat, a Courtier and London’s Customs Officer. He lived with his wife in the Chamber above the Gate in the City Wall at Aldgate. His poetry shows a rugged, joyous medieval England including many scenes reflecting life in London. His stories document the ending of the feudal system, growing dissatisfaction with the corruption in the Church, and shows the robust independence with which the English led their lives.
His work helped change the fashion from poetry in French or Latin to acceptance of the English language as suitable literary language. This was helped by the growth of literacy in London as its Merchants and Guildsmen became increasingly successful. In 1422, for example, the Brewers decided to keep their records in English ‘as there are many of our craft who have the knowledge of reading and writing in the English idiom.’
Chaucer and other poets such as Langland give a vivid portrait of Medieval London which was dynamic, successful but also torn by crisis such as the Lollard challenge to Catholic hegemony, and the Peasants who revolted against oppression as the ruling classes struggled to resist the increased independence of the working people following the Black Death.
A walk which explores London in the Middle Ages, We begin at Aldgate, and follow Chaucer from his home to his place of work at the Customs House, and then to St Thomas Chapel on London Bridge, and across the River to where the Canterbury Tales start – at the Tabard Inn.
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude
London before and after The Roman Invasion

October 29th
The walk looks into the evidence for a prehistoric London and tells the story of the coming of the Romans in AD43
The walk is led by Kevin Flude, a former archaeologist at the Museum of London.
The walk investigates the City of London before and after the the Roman Conquest. What is the evidence for settlement before the Romans set up town of Londinium? Why did the Romans establish the town on this spot? Who were the early Roman Londoners and what made their choice of site so successful?
The fledgling Town was then burnt down by Queen Boudiccan and her Icenian rebels. We look at the evidence for the Revolt and London’s recovery to became the capital of Britain.
This is a London Walks Guided Walk. Look at their web site for a list of other of their amazing walks.
REVIEWS (from London Walks website)
“Kevin, I just wanted to drop you a quick email to thank you ever so much for your archaeological tours of London! I am so thrilled to have stumbled upon your tours! I look forward to them more than you can imagine! They’re the best 2 hours of my week! 🙂 Best, Sue
London Before London – Prehistoric London Virtual Walk

October 29th
An exploration of London before the foundation of Londinium
It was long thought that London was founded by a Trojan Exile in the Late Bronze Age. But historical analysis and archaeological excavation gradually demoted the idea to a myth.
On this tour we explore what was in the London area before the Romans. We begin at Heathrow and tour Greater London for evidence from the Paleolithic to the invasion of the Emperor Claudius.
We concentrate on the period since the introduction of farming, and bring together evidence for the prehistoric Kingdoms that controlled the area on the eve of the Invasion. We look for henges, barrows, hill forts, hut circles and look at genetic evidence for identity of prehistoric Londoners. The tour will end in the City.
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude, ex Museum of London Archaeology and Museum Curator
The Peasants Revolt Anniversary Guided Walk (virtual tour on the same day at 7.30)
Aldersgate Underground Sunday 11th June 2023 10.45am
A Virtual Walk tracking the progress of the Peasants as they take control of London
On the anniversary of the Peasants Revolt we reconstruct the events that shook the medieval world. In June 1381, following the introduction of the iniquitous Poll Tax, England’s government nearly fell, shaken to the core by a revolt led by working men. This dramatic tour follows the events of the Revolt as the Peasants move through London in June 1381.
We met up with the Peasants at Aldgate, force our way into the City. We march on the Tower of London as the King makes concessions by ending serfdom, at Mile End. But the leaders take the mighty Tower of London and behead the leaders of Richard’s government. Attacks follow on the lawyers in the Temple, the Prior at St. John’s of Jerusalem, Flemish Londoners, and on Lambeth and Savoy Palaces.
The climax of the Revolt comes at Smithfield where a small Royal party confront the 30,000 peasants.
To Book:
Tudor London – The City of Wolf Hall
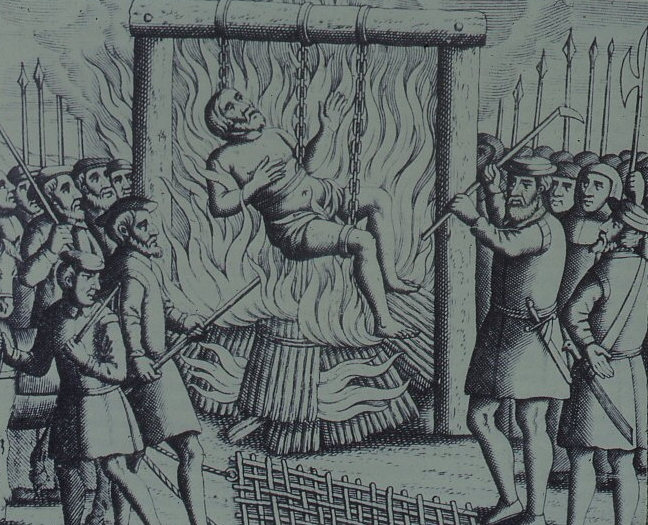

Friday 28 April And June 4th 2023 5.15pm Barbican Underground Station
The Walk creates a portrait of London in the early 16th Century, with particular emphasis on the life and times of Thomas Cromwell and Thomas More
More and Cromwell had much in common, both lawyers, commoners, who rose to be Lord Chancellor to Henry VIII, and ended their careers on the block at Tower Hill.
The walk starts with an exploration of Smithfield – site of the stake where Heretics were burnt alive and to St Bartholomew’s Monastery – given to Richard Rich after his decisive role in the downfall of Thomas More. We continue to St Paul where Martin Luther’s books where burnt, and later, were Puritans attacked dancing round the Maypole. We walk along the main markets streets of London, to Thomas More’s birthplace, and to the site of More’s and Cromwell’s townhouses before, if time allows, finishing at the site of the Scaffold where More and Cromwell met their ends.
Myths & Legends of London May Eve Special Guided Walk

Sunday 30th April 2023 3.00pm Tower Hill Tube Station
The walk tells the story of London’s legendary past, explores May Day and the Celtic Festival of Beltane
The walk is led by Kevin Flude, a former archaeologist at the Museum of London, who has an interest both in the archaeological evidence as well as the myths and legends of London’s origin.
The walk is one of a series about London’s Myths and Legends which take place on or around one of the significant festivals of the calendar. On this walk we celebrate May Day, or Beltane – the celebration of the coming of Summer.
The walk begins with the tale of London’s legendary origins in the Bronze Age by an exiled Trojan called Brutus. Stories of Bladud, Bellinus, Bran, Vortigern and Arthur will be interspersed with how they fit in with archaeological discoveries. As we explore the City we also look at evidence for ‘Celtic’ origins of London and how May Day may have been celebrated in London.
The route starts at Tower Hill, then down to the River Thames at Billingsgate, to London Bridge and Southwark Cathedral, into the valley of the River Walbrook, past the Temple of Mithras, along Cheapside towards the Roman Amphitheatre and St Pauls.
This is a London Walks guided walk. Look at their web site for a list of other of their amazing walks.
REVIEWS (from London Walks website)
“Kevin, I just wanted to drop you a quick email to thank you ever so much for your archaeological tours of London! I am so thrilled to have stumbled upon your tours! I have wanted to be an archaeologist since 1978 at the ripe old age of 8 years,… I was told for years that I could not be an archaeologist [for any number of reasons, which I now realise are completely ridiculous!], so I ended up on a different course of study. And now at the age of 50, it is my one great regret in life. So, I am thoroughly enjoying living vicariously through you, the digs you’ve been on, and the history you bring to life for us! British archaeology would have been my specific area of study had I pursued it. ?? Thank you SO MUCH for these! I look forward to them more than you can imagine, and honestly, I’ll be sad if you get them down to 1.5 hours! They’re the best 2 hours of my week! 🙂 Best, Sue
To Book:
Myths, Legends of London May Day Special Virtual Tour
Monday 1st May 2023 7.30pm
The virtual tour tells the story of London’s myths and legends and the Celtic Festival of Beltane
The virtual tour is led by Kevin Flude, a former archaeologist at the Museum of London, who has an interest both in the archaeological evidence as well as the myths and legends of London’s origin.
It is one of a series about London’s Myths and Legends which take place on or around one of the significant festivals of the Celtic calendar. On this tour we celebrate May Day, or Beltane – the celebration of the coming of Summer.
The walk begins with the tale of London’s legendary origins in the Bronze Age by an exiled Trojan called Brutus. Stories of Bladud, Bellinus, Bran, Vortigern and Arthur will be interspersed with how they fit in with archaeological discoveries. As we explore the City we also look at evidence for ‘Celtic’ origins of London and how May Day was celebrated in London.
The virtual route starts at Tower Hill, then down to the River Thames at Billingsgate, to London Bridge and Southwark Cathedral, to the Roman Forum at the top of Cornhill, into the valley of the River Walbrook, passed the Temple of Mithras, along Cheapside to the Roman Amphitheatre, and finishing up in the shadow of St Pauls
This is a London Walks Virtual Walk. Look at their web site for a list of other of their amazing walks.
To Book:
https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/myths-and-legends-of-london-special-may-day-virtual-tour-tickets-601341648057
Chaucer’s Medieval London Guided Walk
Aldgate Underground Sunday 16 April 2023 11.30pm
A Walk around Medieval London following in the footsteps of its resident medieval poet – Geoffrey Chaucer
One of the spectators at the Peasants Revolt was Geoffrey Chaucer, born in the Vintry area of London, who rose to be a diplomat, a Courtier and London’s Customs Officer. He lived with his wife in the Chamber above the Gate in the City Wall at Aldgate. His poetry shows a rugged, joyous medieval England including many scenes reflecting life in London. His stories document the ending of the feudal system, growing dissatisfaction with the corruption in the Church, and shows the robust independence with which the English led their lives.
His work helped change the fashion from poetry in French or Latin to acceptance of the English language as suitable literary language. This was helped by the growth of literacy in London as its Merchants and Guildsmen became increasingly successful. In 1422, for example, the Brewers decided to keep their records in English ‘as there are many of our craft who have the knowledge of reading and writing in the English idiom.’
Chaucer and other poets such as Langland give a vivid portrait of Medieval London which was dynamic, successful but also torn by crisis such as the Lollard challenge to Catholic hegemony, and the Peasants who revolted against oppression as the ruling classes struggled to resist the increased independence of the working people following the Black Death.
A walk which explores London in the Middle Ages, We begin at Aldgate, and follow Chaucer from his home to his place of work at the Customs House, and then to St Thomas Chapel on London Bridge, and across the River to where the Canterbury Tales start – at the Tabard Inn.
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude
Archaeology of London Guided Walk

Sunday 16th April and 4th June 2023 2.30 Exit 3 Bank Underground Station
Legend says that London was founded as New Troy. Historians believed it was founded as Londinium after the Bridge was built by the legionaries of the Emperor Claudius in AD 43. Archaeologists in the 1970s and 1980s discovered that London was refounded as Lundenwic in the 7th Century and again in the 9th Century when it was called Lundeburg.
This walk tells the epic tale of the uncovering of London’s past by Archaeologists. And provides an insight into the dramatic history of the Capital of Britannia, and how it survived revolts, fires, plagues, and reacted to the decline and fall of the Roman Empire. It became the foremost English City but with periods under Viking and Norman control.
We tell the story in the streets of the City of London, beginning in the valley of the River Walbrook by the Temple of Mithras, and visit many sites where important archaeological discoveries were made, including the Roman Forum, Amphitheatre. Bath Houses, Temples, Roman roads and the City Walls.
Chaucer’s London To Canterbury Virtual Pilgrimage
Sunday 16th April 2023 7.30pm
A Virtual Walk from Chaucer’s London on pilgrimage along the route of the the Canterbury Tales to Canterbury
One of the spectators at the Peasants Revolt was Geoffrey Chaucer, born in the Vintry area of London, who rose to be a diplomat, a Courtier and London’s Customs Officer. He lived with his wife in the Chamber above the Gate in the City Wall at Aldgate, while he wrote the Canterbury Tales.
His poetry shows a rugged, joyous medieval England including many scenes reflecting life in London.
His stories document the ending of the feudal system, growing dissatisfaction with the corruption in the Church, and shows the robust independence with which the English led their lives, following the Black Death.
A walk which explores London in the Middle Ages, and takes us on the pilgrimage to Canterbury. We begin at Aldgate, and follow Chaucer from his home to his place of work at the Customs House. We cross to Southwark via the famous London Bridge where we start the Pilgrimage at St Thomas Chapel. Then to the Tabard to meet the Pilgrims and onto the Old Kent Road to Canterbury.
This is a London Walks event. Look at their web site (www.walks.com) for a list of other of their amazing walks.
Archaeology of London Guided Walk Sunday 2nd April 2023 11:15 Exit 3 Bank Underground Station
A TALE OF FOUR CITIES
Legend says that London was founded as New Troy. Historians believed it was founded as Londinium after the Bridge was built by the legionaries of the Emperor Claudius in AD 43. Archaeologists in the 1970s and 1980s discovered that London was refounded as Lundenwic in the 7th Century and again in the 9th Century when it was called Lundeburg.
This walk tells the epic tale of the uncovering of London’s past by Archaeologists. And provides an insight into the dramatic history of the Capital of Britannia, and how it survived revolts, fires, plagues, and reacted to the decline and fall of the Roman Empire. It became the foremost English City but with periods under Viking and Norman control.
We tell the story in the streets of the City of London, beginning in the valley of the River Walbrook by the Temple of Mithras, and visit many sites where important archaeological discoveries were made.
Jane Austen’s London
Sat 2.30 pm 02/04/23 Green Park underground station, London (north exit, on the corner)
An exploration of Mayfair, the centre of the London section of Sense & Sensibility and where Jane came to visit her brother
“It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a Jane Austen devotee in possession of the good fortune of a couple of free hours today must be in want of this walk.”
People associate Jane Austen and her characters with a rural setting. But London is central to both Jane Austen’s real life and her literary life. So, this tour will explore Jane’s connections with London and give the background to Sense and Sensibility, a good part of which is based in this very area. We begin with the place Jane’s coach would arrive from Hampshire, and then walk the streets haunted by Willougby; past shops visited by the Palmers, the Ferrars; visit the location of Jane Austen’s brother’s bank and see the publisher of Jane’s Books. The area around Old Bond Street was the home of the Regency elite and many buildings and a surprising number of the shops remain as they were in Jane Austen’s day.
This is a London Walk Guided Walk lead by Kevin Flude
CHAUCER’S MEDIEVAL LONDON VIRTUAL WALK

Sunday 12 February 2023 7.30pm
A Virtual Walk around Medieval London following in the footsteps of its resident medieval poet – Geoffrey Chaucer
One of the spectators at the Peasants Revolt was Geoffrey Chaucer, born in the Vintry area of London, who rose to be a diplomat, a Courtier and London’s Customs Officer. He lived with his wife in the Chamber above the Gate in the City Wall at Aldgate. His poetry shows a rugged, joyous medieval England including many scenes reflecting life in London. His stories document the ending of the feudal system, growing dissatisfaction with the corruption in the Church, and shows the robust independence with which the English led their lives.
His work helped change the fashion from poetry in French or Latin to acceptance of the English language as suitable literary language. This was helped by the growth of literacy in London as its Merchants and Guildsmen became increasingly successful. In 1422, for example, the Brewers decided to keep their records in English ‘as there are many of our craft who have the knowledge of reading and writing in the English idiom.’
Chaucer and other poets such as Langland give a vivid portrait of Medieval London which was dynamic, successful but also torn by crisis such as the Lollard challenge to Catholic hegemony, and the Peasants who revolted against oppression as the ruling classes struggled to resist the increased independence of the working people following the Black Death.
A walk which explores London in the Middle Ages, We begin at Aldgate, and follow Chaucer from his home to his place of work at the Customs House, and then to St Thomas Chapel on London Bridge, and through London to Poultry, Bucklersbury and Cheapside before visiting the Guildhall and St Pauls. We will walk in the muddy City Streets, exploring the unhealthy conditions and poverty amidst great riches and pageantry.
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude
THE REBIRTH OF SAXON LONDON ARCHAEOLOGY VIRTUAL WALK

Sunday 29 January 2023 7.30pm
An exploration of what happened following the Roman Period. How did a Celtic speaking Latin educated Roman City become, first deserted, then recovered to become the leading City in a germanic speaking Kingdom?
The Romans gave the name of Saxons to the barbarian pirates that plagued the North Sea region in the Late Roman Period. Historians link them with the Angles and Jutes who, according to the Venerable Bede, conquered the Roman Province of Britannia and turned it into England. London became its leading town.
But excavation and DNA analysis make the traditional story more difficult to sustain and although the Anglo-Saxons have a rich history how much of it can be trusted? Was there a Dark Age? Or was it just a ‘transition’ from Roman to English? How did English become the main language sweeping aside native Celtic and Latin languages? Much of the story of Saxon London has been founded on myth and dubious historical sources, but archaeological, documentary and genetic research are, perhaps, beginning to provide a clearer narrative.
Following the fall of Roman Britain, London was almost deserted. On this walk we explore how London recovered and grew to be the most important City in England by 1066. We begin our walk in the heart of the City at Bank, and walk through the City to St Pauls, Then along Fleet Street and the Strand to Covent Garden..
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude, ex Museum of London Archaeology and Museum Curator
The Decline And Fall Of Roman London Archaeology Virtual Walk

Sunday 22nd January 11.30am Exit 2 St Pauls Underground Station
An exploration of what happened at the end of the Roman Period, and how the City became deserted, and then, reborn as an English City.
The first British Brexit? The Roman Britons kicked out the Romans in 407AD, and, soon, asked them to come back after a catastrophic collapse. Faced with plaque, civil war, invasion, mass immigration, industrial decline, reversion to barter; the authorities struggled against anarchy and descent into a dark age.
But was that how it was? Wasn’t it a rather a transition into the Late Antique period in which life for most people went on much as before except paying taxes to local rulers rather than distant Romans?
The walk investigates why the Roman system in London broke down, and what really was the impact of the end of the Roman system in London? What is the evidence? and can we trust it? Or can we really do nothing much more than guess?
We tramp the streets of London in search of light to shine on the dark age of London.
The Decline And Fall Of Roman London Archaeology Virtual Walk

Sunday 22nd January 7:00pm
An exploration of what happened at the end of the Roman Period, and how the City became deserted, and then, reborn as an English City.
The first British Brexit? The Roman Britons kicked out the Romans in 407AD, and, soon, asked them to come back after a catastrophic collapse. Faced with plaque, civil war, invasion, mass immigration, industrial decline, reversion to barter; the authorities struggled against anarchy and descent into a dark age.
But was that how it was? Wasn’t it a rather a transition into the Late Antique period in which life for most people went on much as before except paying taxes to local rulers rather than distant Romans?
This virtual walk explores why the Roman system in London broke down, and what really was the impact of the end of the Roman system in London? What is the evidence? and can we trust it? Or can we really do nothing much more than guess?
We tramp the virtual streets of London in search of light to shine on the Dark Ages in London.
London Before And After The Roman Invasion

Tower Hill Underground Sunday 8th January 2023 11.30pm
The walk looks into the evidence for a prehistoric London and tells the story of the coming of the Romans in AD43
The walk is led by Kevin Flude, a former archaeologist at the Museum of London.
The walk investigates the City of London before and after the the Roman Conquest. What is the evidence for settlement before the Romans set up town of Londinium? Why did the Romans establish the town on this spot? Who were the early Roman Londoners and what made their choice of site so successful?
The fledgling Town was then burnt down by Queen Boudiccan and her Icenian rebels. We look at the evidence for the Revolt and London’s recovery to became the capital of Britain.
This is a London Walks Guided Walk. Look at their web site for a list of other of their amazing walks.
REVIEWS (from London Walks website)
“Kevin, I just wanted to drop you a quick email to thank you ever so much for your archaeological tours of London! I am so thrilled to have stumbled upon your tours! I look forward to them more than you can imagine! They’re the best 2 hours of my week! 🙂 Best, Sue
London Before London – Prehistoric London Virtual Walk
Sunday 8th January 7pm
An exploration of London before the foundation of Londinium
It was long thought that London was founded by a Trojan Exile in the Late Bronze Age. But historical analysis and archaeological excavation gradually demoted the idea to a myth.
On this tour we explore what was in the London area before the Romans. We begin at Heathrow and tour Greater London for evidence from the Paleolithic to the invasion of the Emperor Claudius.
We concentrate on the period since the introduction of farming, and bring together evidence for the prehistoric Kingdoms that controlled the area on the eve of the Invasion. We look for henges, barrows, hill forts, hut circles and look at genetic evidence for identity of prehistoric Londoners. The tour will end in the City.
This is a London Walks event by Kevin Flude, ex Museum of London Archaeology and Museum Curator
A New Year Walk on the Myths, Legends and the Origins of London

Sunday 1st January 2023 2.00pm Tower Hill Underground
The walk tells the stories of London’s myths, legends and archaeology to find out what they say about the origins of London. As its New Year we also look at New Year as it was celebrated in London through the ages.
The walk is led by Kevin Flude, a former archaeologist at the Museum of London, who has an interest both in myths, legends and London’s Archaeology.
The walk will tell the story of the legendary origins of London which record that it was founded in the Bronze Age by an exiled Trojan called Brutus. The new City was called Troia Nova or New Troy, which became corrupted to Trinovantum, and then changed to Lud’s Dun or London. When the Roman system broke down in 410 AD, historical records were almost non-existent, until the Venerable Bede recorded the building of St Pauls Cathedral in 604 AD. The two hundred year gap, has another rich selection of legends. The walk will explore these stories and compare the legends with Archaeological discoveries. We also look at New Year Customs and Folklore, and the arrangements of the Calendar for different cultures.
The route starts at Tower Hill, then down to the River at Billingsgate, London Bridge, and into the centre of Roman London.
This is a London Walks Guided Walks. Look at their web site for a list of other of their amazing walks both physical and virtual.
Ring in the New Year Virtual Walk

Sunday 1st January 2023 7.00pm
On this walk we look at how London has celebrated the New Year over the past 2000 years.
The New Year has been a time of review, renewal and anticipation
of the future from time immemorial. The Ancient Britons saw the Solstice as a symbol of a promise of renewal as the Sun was reborn. As the weather turns to bleak mid winter, a festival or reflection and renewal cheers everyone up. This idea of renewal was followed by the Romans, and presided over by a two headed God called Janus who looked both backwards and forwards. Dickens Christmas Carol was based on redemption and his second great Christmas Book ‘The Chimes’ on the renewal that the New Year encouraged.
We look at London’s past to see where and how the New Year was celebrated. We also explore the different New Years we use and their associated Calendars – the Pagan year, the Christian year, the Roman year, the Jewish year, the Financial year, the Academic year and we reveal how these began. We look at folk traditions, Medieval Christmas Festivals, Boy Bishops, Distaff Sunday and Plough Monday, and other Winter Festival and New Year London tradition and folklore.
At the end we use ancient methods to divine what is in store for us in 2023..
The walk finds interesting and historic places in the City of London to link to our stories of Past New Year’s Days. We begin with the Druids at Tower Hill, and walk around the Roman City of London, and through London History