The name Lucy is from the same Latin origin (Lucidus) as lucent, lux, and lucid. It means to be bright, or to shine. It is similar to the Ancient Greek λευκός (leukós, “white, blank, light, bright, clear”. Luke has the same origins (bright one, bringer of light and light of the sacred flame) and is very appropriate for the most literate of the evangelists. At this time of the year, we are in need of a festival with bright lights to cheer us up!
And St Lucy’s Day is the beginning of the winter festival that culminates with the Solstice, where the old sun dies, and the new one is born. December the 13th was the Solstice until Pope Gregory reformed the Calendar in the 16th Century, as nine days were lopped off the year of transition.
The festival of Sankta Lucia is particularly popular in Sweden, where Dec 13th is thought to be the darkest night. Every year, the Swedish community in the UK has a service to Lucia in St Pauls. I have several times tried to get tickets, but so far, have failed miserably. But if you look lower down, you will see a link to the beautiful procession and service at St Pauls.
I found out about Sankta Lucia from a Swedish choir who hired me to do a tour of the City of London some years ago. I took them into Christopher Wren’s marvellous St Stephen’s Church and, under the magnificent Dome, they fancied the acoustics and spontaneously sang. I recorded a snatch of it.
Recent medical research has shown the importance of light, not only to our mental health but to our sleep health, and recommends that work places need to have a decent light level with ‘blue light’ as a component of the lighting. It is also an excellent idea to help your circadian rhymes by going for a morning walk, or morning sun bathing, even on cloudy days.
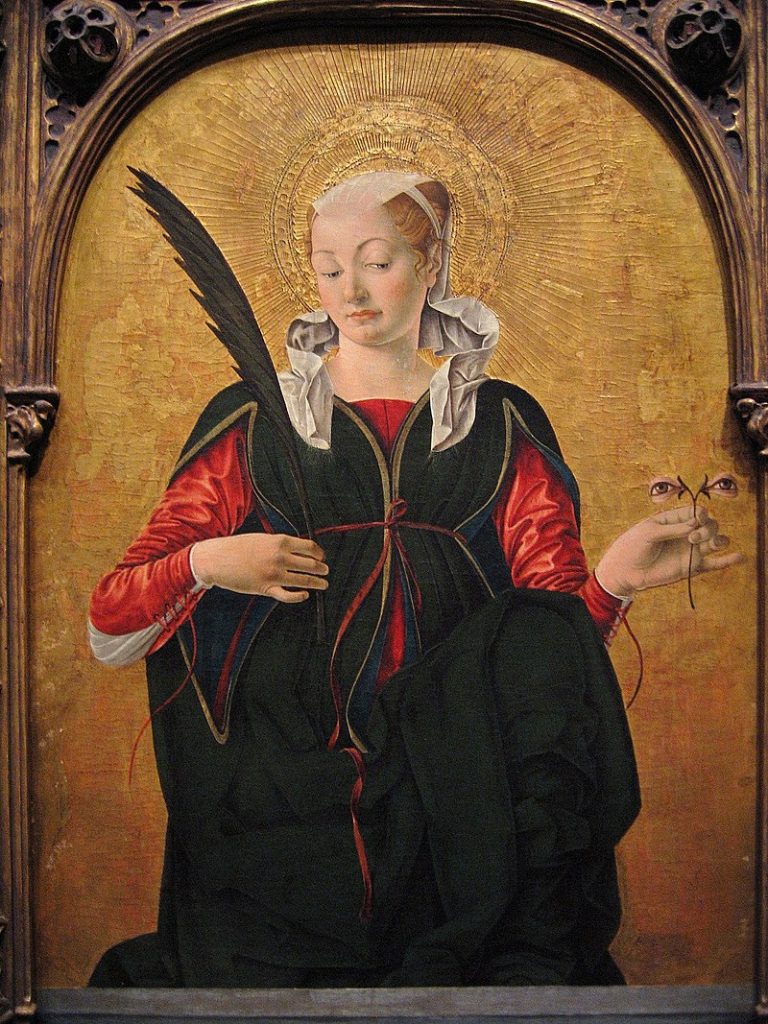
St Lucy is from Syracuse in Sicily, said to be a victim of the Diocletian Persecution of Christians in the early 4th Century. She is an authentic early martyr, although details of her story cannot be relied upon as true. She was said to be a virgin, who was denounced as a Christian by her rejected suitor, miraculously saved from serving in a brothel, then, destruction by fire, but did not escape having her eyes gouged out. Finally, her throat was cut with a sword. Her connection to light (and the eye gouging) makes her the protectress against eye disease, and she is often shown holding two eyes in a dish.
St. Aldhelm (English, died in 709) puts St Lucy in the list of the main venerated saints of the early English Church, confirmed by the Venerable Bede (English, died in 735). Her festival was an important one in England ‘as a holy day of the second rank in which no work but tillage or the like was allowed’.[1]
Roman Hoodie ~Part two – the Sequani

Yesterday I made a long digression which began with a discussion of Roman Winter clothing. Our picture of the hoodie from a tombstone in Cirencester, said it was of
Philus, son of Cassavus, a Sequanian, aged 45, lies buried here.
Roman Inscriptions of Britain.org
One of our readers from France alerted me to the Wikipedia page on the Sequani which explains that the name comes from the Goddess Sequana who is a water goddess. The centre of the territory is Besançon which is on the Doubs River part of the Haute Saône Doubs and near to the springs that are the source of the Seine (west of Dijon). Here, the Fontes Sequanae (“The Springs of Sequana”) gave her name to the River Seine, and a healing spring was established in the 2nd/1st BC. Enlarged by the Romans, it became a significant health centre. as Wikipedia explains in the clip below:

‘Many dedications were made to Sequana at her temple, including a large pot inscribed with her name and filled with bronze and silver models of parts of human bodies to be cured by her. Wooden and stone images of limbs, internal organs, heads, and complete bodies were offered to her in the hope of a cure, as well as numerous coins and items of jewellery. Respiratory illnesses and eye diseases were common. Pilgrims were frequently depicted as carrying offerings to the goddess, including money, fruit, or a favourite pet dog or bird.’
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequana
First Posted on December 13th, 2022, updated on December 13th 2023


















![By JanesDaddy (Ensglish User) - English Wikipedia - [1], CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1663124](https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/1280px-Eels_1385-1024x768.jpg)



