The Royal Africa Company was set up with a monopoly on trade with the west coast of Africa in:
“redwood, elephants’ teeth, negroes, slaves, hides, wax, guinea grains, or other commodities of those countries”
On January 10th. 1663 King Charles II affirmed the new charter for the Company that, above all else, was responsible for British continuing involvement in slavery. Shareholders included his nephew, Prince Rupert, Samuel Pepys, and much of the British Establishment, Aristocracy, and City Merchants. Its headquarters were in Cornhill, not far from the East India Company’s HQ. The company was closed in 1752.
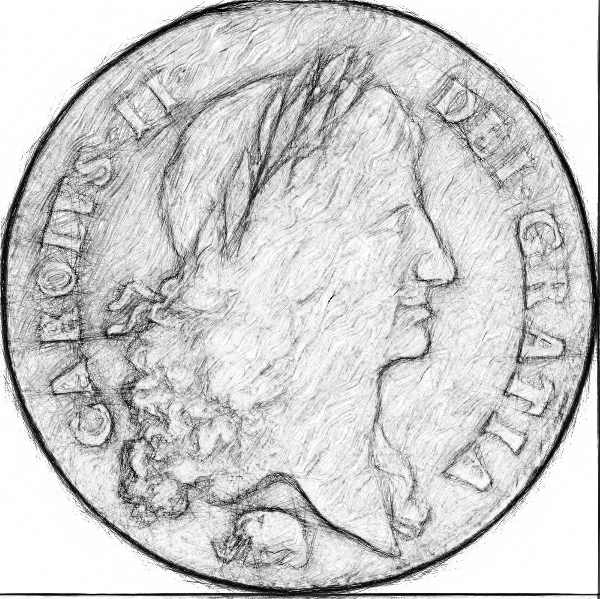
Gold from the Gold Coast was used to make coins, which became known as ‘guineas’. They were originally made from one quarter of an ounce of gold. Below is a sketch of a two guinea coin from the reign of Charles II. Note the elephant at the bottom of the coin.
The guinea was original worth 1 pound but fluctuated with the price of Gold. Pepys records it at 24 or 25 shillings. It was eventually phased out, but it became a posh way of expressing value. Ordinary goods would be priced in pounds, but expensive ones in Guineas. By then valued at 21 shillings. (£1 pound 5 pence). Wikipedia suggests it was used for ‘prices of land, horses, art, bespoke tailoring, furniture, white goods and other “luxury” items’. I remember going shopping with my parents in London and wondering at the fur coats being priced in Guineas. It died out, as a practice, in the 70s.

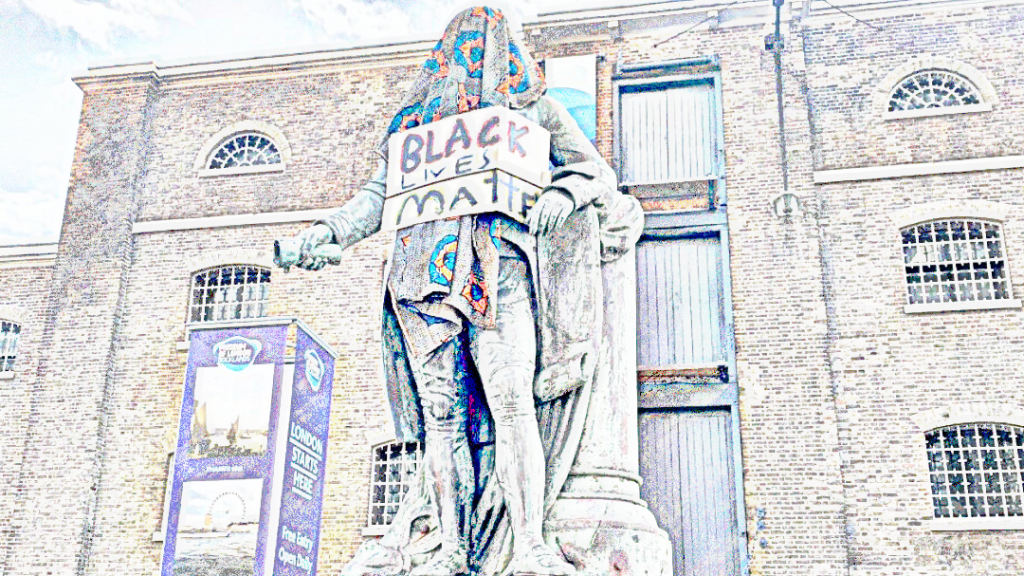
There are many sites giving a history of slavery, and the British involvement with it, which I encourage everyone to investigate. But, here, I would just like to point out, how involved the British Royal Family was in the trade. Also, to note that the British education system has emphasised the role of Britain in the abolition of slavery, rather than our involvement in setting it up and continuing it. This has begun to change, and a new generation of school children in London can visit the excellent London: Sugar & Slavery Gallery at the Museum of London in Docklands.
University College, London has undertaken a profound project where they took the records of compensation payments to:
The slaves? No, not to them but to the slave owners! UCL have created a resource where you can click on the streets of London and other areas, to find out the holders of slaves in that street. The compensation of £20m pounds is probably around £16billion in modern terms, and it makes me believe that the least we can do is to fund projects to correct the educational and life disadvantages of people and countries impacted by slavery to the tune of £16 billion.
I have just looked for the closest slave owner in my area of the East End of London, and it is about 500 yards away from me. Here are the abridged details from the database. It is very simple to use. Have a go by following the link below.
Solomon Nunes Flamengo of Kingston, living at Mutton Lane in Hackney when he wrote his will in 1778. Merchant. Estate probated in Jamaica in 1779. Slave-ownership at probate: 6 of whom 2 were listed as male and 4 as female. 4 were listed as boys, girls or children. Total value of estate at probate: £21356.26 Jamaican currency of which £332.5 currency was the value of enslaved people.
Presumably, the value of his compensation was £332.5. Solomon was Jewish, which is unusual for the records, by far the majority being Christian. I chose Solomon to show simply because he was the closest to my house.
Please do have a look at the UCL website:
Britain began regulating the Slave trade in the late 18th Century, abolished the Slave Trade in 1807. Slavery, with the compensation to slave owners in 1833, was abolished but they replaced slavery with apprenticeship – in effect bound labour. This was ended in 1838.For more details look at https://www.parliament.uk/
Finally, I have been updating, revising and republishing many posts which you might enjoy reading before Christmas and the New Year seem too far in the past!
- Apples & if the frost be very extreame January 9th 2024
- Plough Monday January 8th 2024
- St Distaff’s Day & the Triple Goddesses, January 7th 2024
- A Radical Twelfth Night January 6th 2024
- Twelfth Night? Time to take down your Christmas decorations, January 5th 2024
- Last chance to make the Twelfth Night cake & the night skies, January 4th 2024
- Prophecy January 3rd 2024
- St. Genevieve’s Day and St Germanus January 3rd 2024
- Archive of Events and Walks 2nd January 2024
- The French Revolution’s Solar Year — January 2nd 2024
- 9th Day of Christmas or is it? January 2nd 2024
- New Years Day Almanacs January 1st 2024
- New Years Eve December 31st 2024

