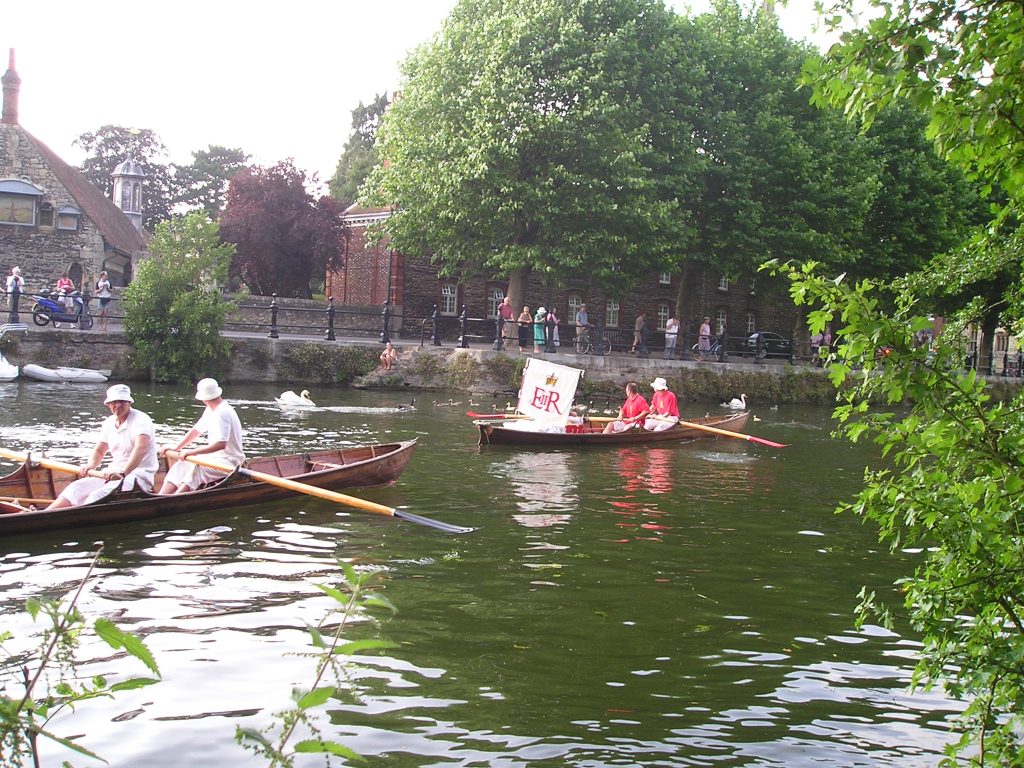
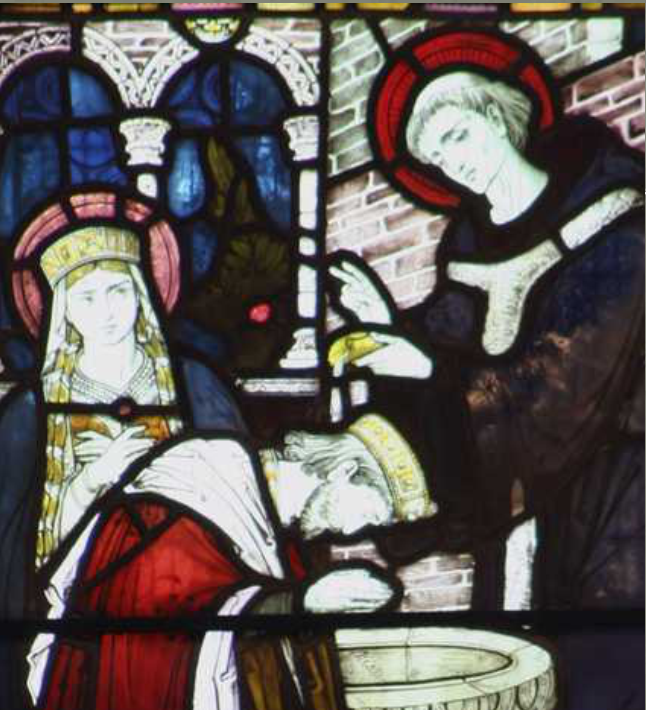
Swan upping takes place on the 3rd Week of July. It is an annual census of the Swans on the River Thames. This year it began on Monday, July 14th. It began in the 12th Century.
In theory, the King has the ownership of all unmarked Mute Swans on open water in the UK. Swan Upping is an ancient ceremony during which Swans are upped, checked for health and ringed if they do not belong to the King. In fact, it is the Cygnets which are upped. They are checked for weight and health. Their parents are checked for an ownership ring. If the parents are ringed then the young cygnets will be ringed accordingly. If the parents are not ringed, then they belong to the King and remain unringed.
This ceremony now only takes place on the Thames. It begins at Sunbury and progresses to Abingdon. The Swan Uppers have traditional wooden rowing skiffs and a scarlet Upping Shirt. They are managed by the Swan Marker. The Royal Uppers are accompanied by Swan Uppers from the two City Livery Companies that still have rights to ownership of Thames Mute Swans. These companies are the Dyers Company and the Vintners Company.
If you want to catch Swan Upping this year you will find them upping Swans at the following places:
Thursday 17th July 2025
Sonning-on-Thames 09.00 – Departure point
Caversham Lock 10.15
Mapledurham Lock 12.30
Goring Lock 17.00
Moulsford 18.00
Friday 18th July 2025
Moulsford 09.00 – Departure point
Benson Lock 10.00
Clifton Hampden Bridge 13.00
Culham Lock 16.15
Abingdon Bridge 17.00
King Charles is Seigneur of the Swans and you can find more details at https://www.royalswan.co.uk
Swans moult in July and August, and this renders them flightless. This can last for a period of up to 6 weeks. So it makes them a lot easier to up!
The Swannery at Abbotsbury
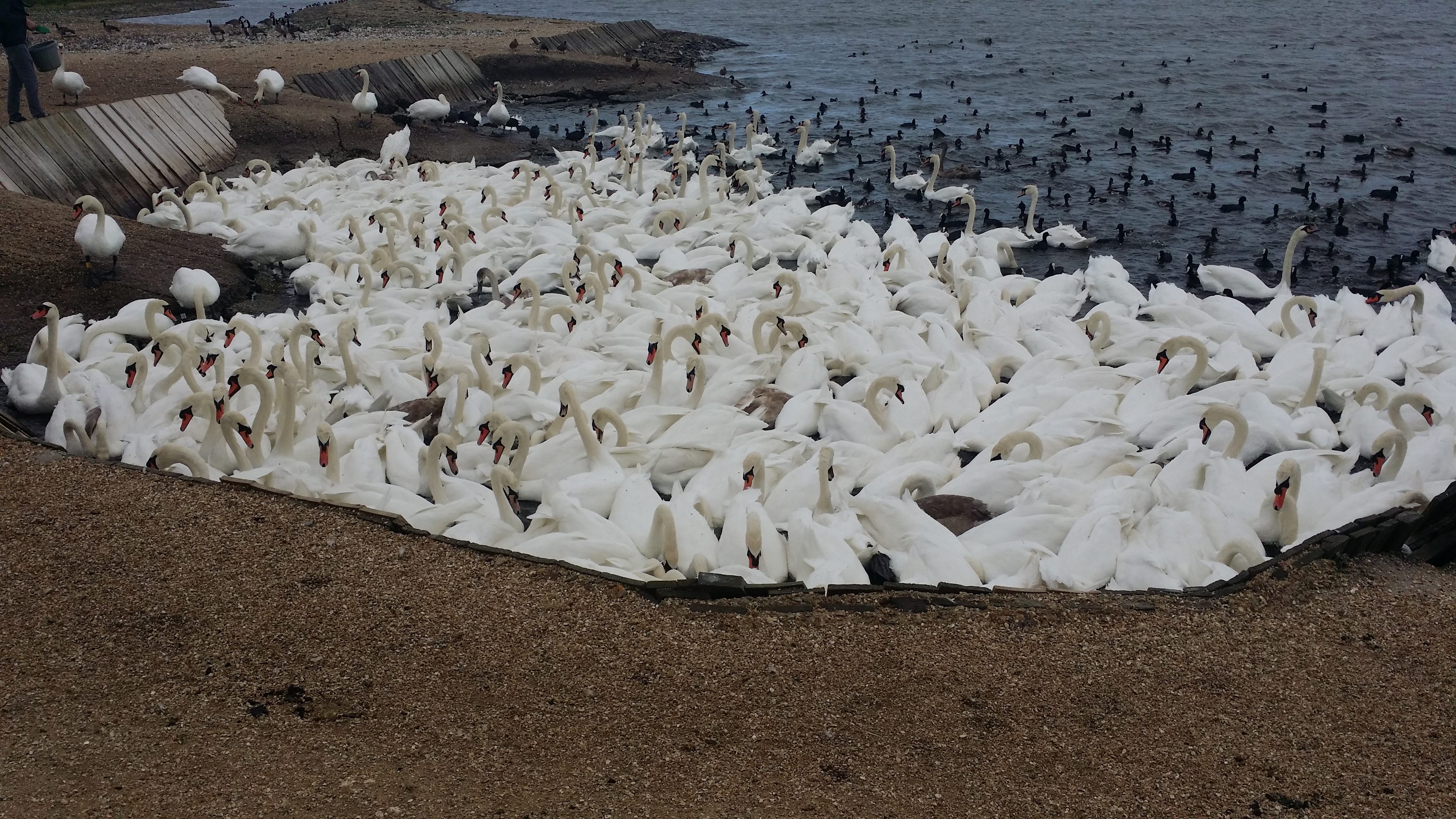

Now I didn’t find that fact on any of the web sites I consulted about Swan Upping. For many years I gave a wonderful programme called Literary Landscapes where we explored lanscapes associated with Jane Austen, Thomas Hardy, Agatha Christie, Conan-Doyle and Charles Dickens. On it, we went to the Swannery at Abbotsbury in Dorset. This was founded by Benedictine Monks in the time of King Cnut. The Strangeways family acquired the Monastery after the Dissolution and still own the Swannery. So they are the fourth authority in the UK who own Swans.
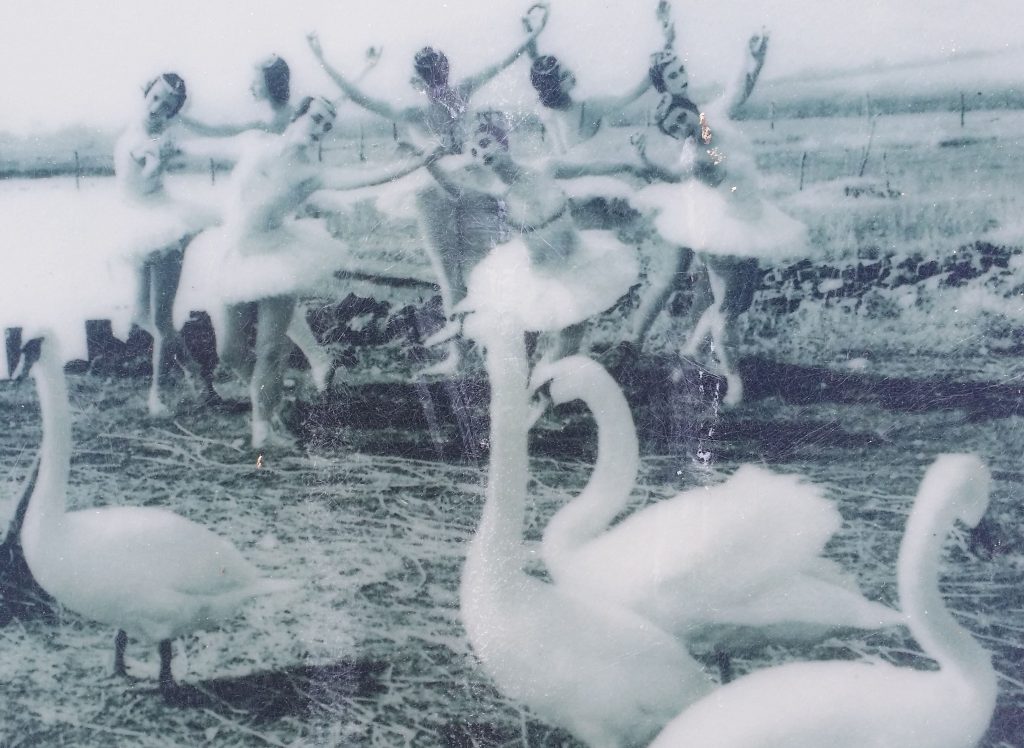
It is a remarkable place, in the heart of Hardy’s Wessex and by the glorious Chesil Beach. Every other year, the Mute Swans are checked and ringed during the flightless period. When Pavlova was working on Swan Lake, she took the dancers to Abbotsbury to observe the behaviour of the Swans.

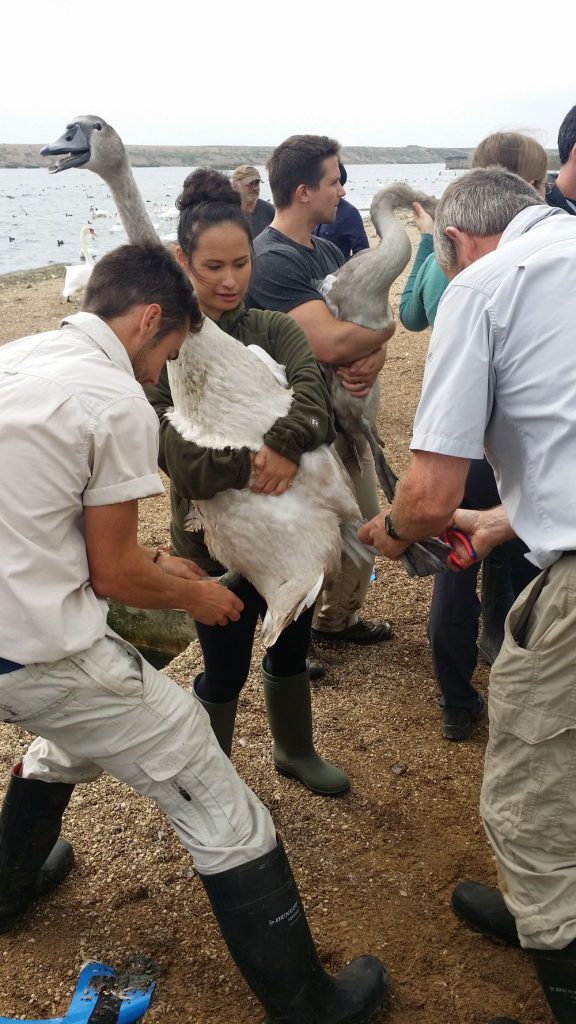
Feathers are collected during the moulting season. They are used by Lloyds Registry, the Society of Calligraphers, illuminators, and other scribes for writing-quills. Other feathers are used by the Plummery to make headdresses for the Royal Bodyguard. They are also used for artists’ brushes, brushes for sweeping bees from honeycomb and arrow flights! (Source: panel at Abbotsbury).

Cartmarking is taking place On Saturday at the Guildhall in London 19th July. For more details of the historic vehicle events: https://thecarmen.co.uk/history/cart-marking/
Created July 16th 2025