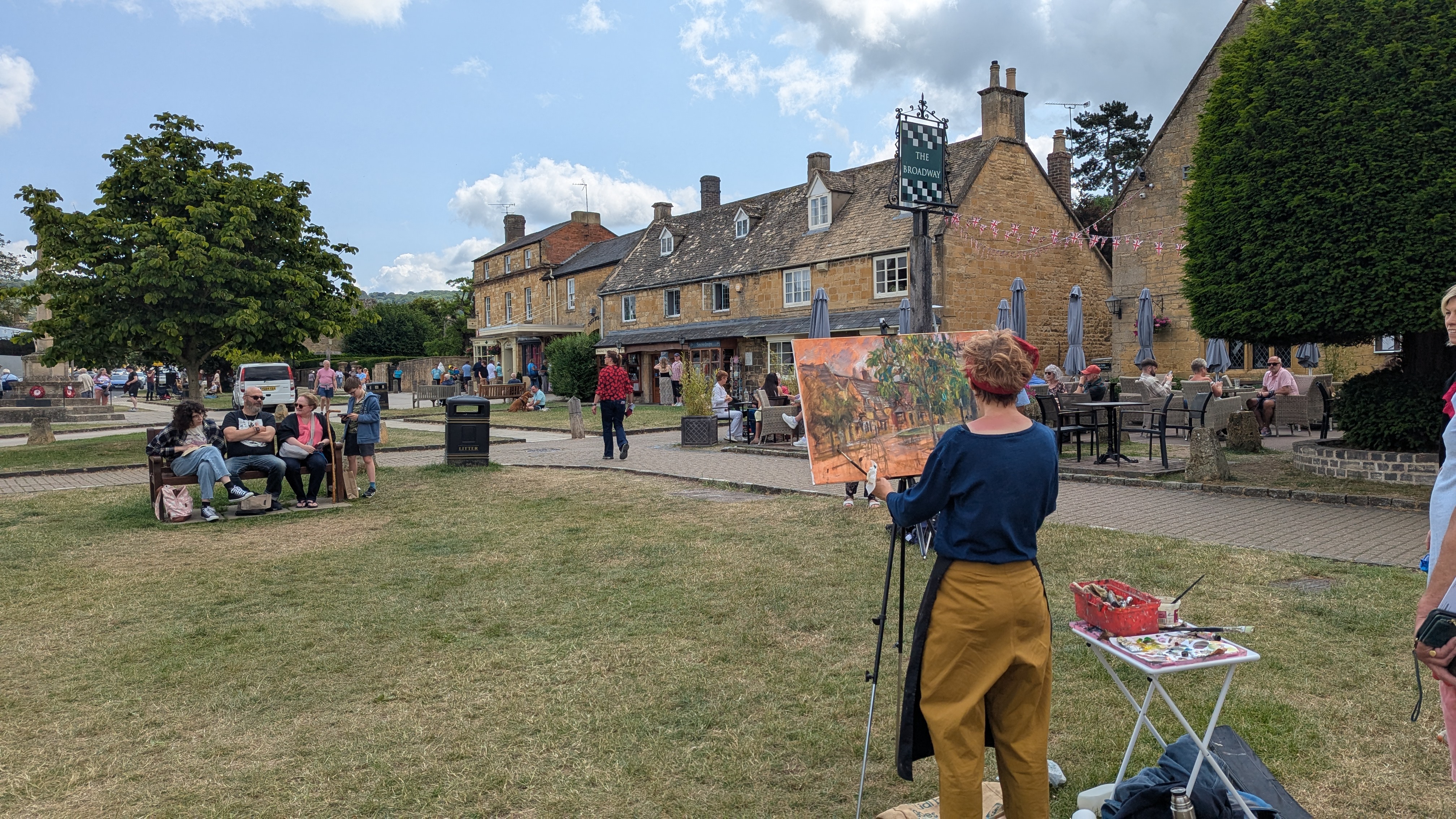
One of the joys of my Summer is revisiting places I know and love in my role as a Course Director for Road Scholar. I first came across the ‘en plein air’ in 2023. On Sunday, June 18th. I was in Broadway, once considered the most beautiful village in Britain. It was also the model for Riseholme in the wonderful Lucia books by E. F. Benson (made into a TV series by the BBC starring Prunella Scales, Geraldine McEwan and Nigel Hawthorne).

The day I visited, in 2025, was last Sunday, June 15th. I have added new photos and revised the texts.
How it Works
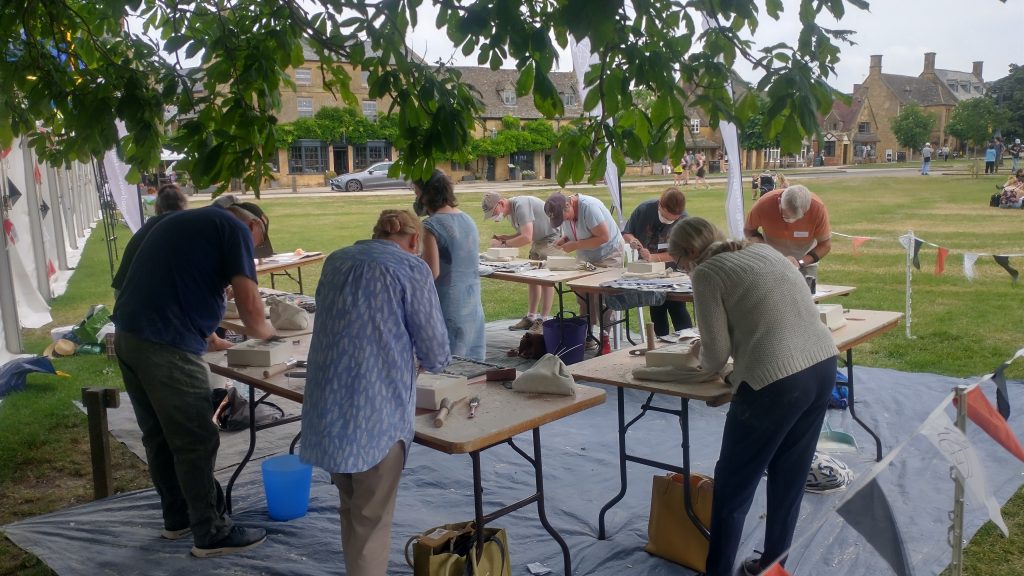
The artists register in the morning and have their paper or canvas stamped, or given a block of Maltese stone. This proves that they have done all the work on the day itself.
This year there were no sculptors. Instead, there were live models in the marquee being painted by portrait painters.
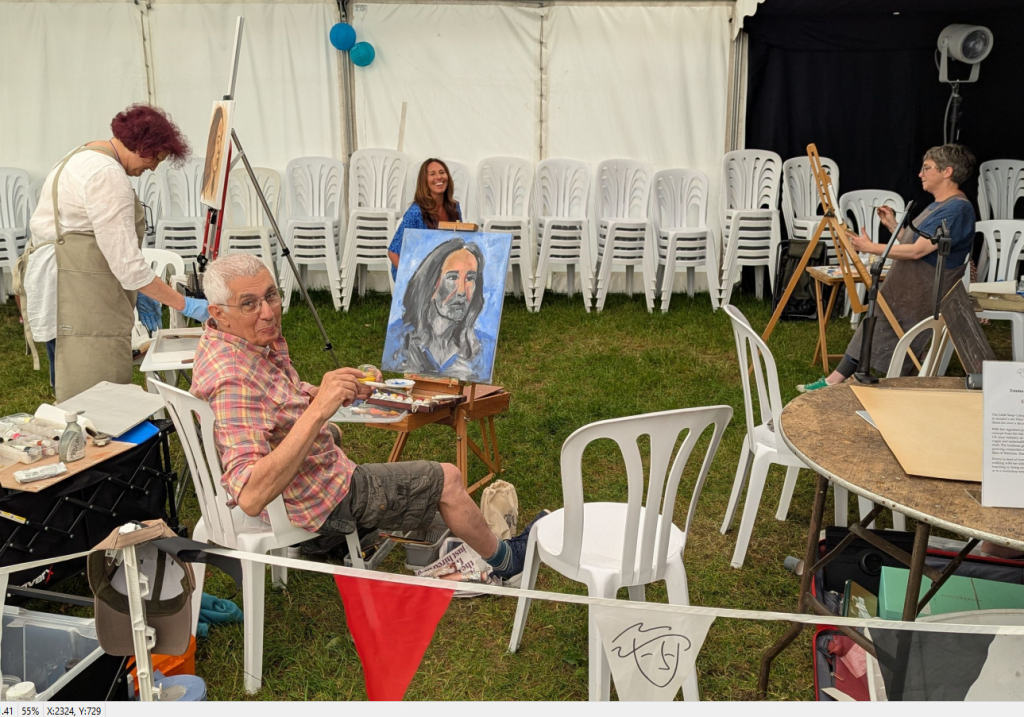

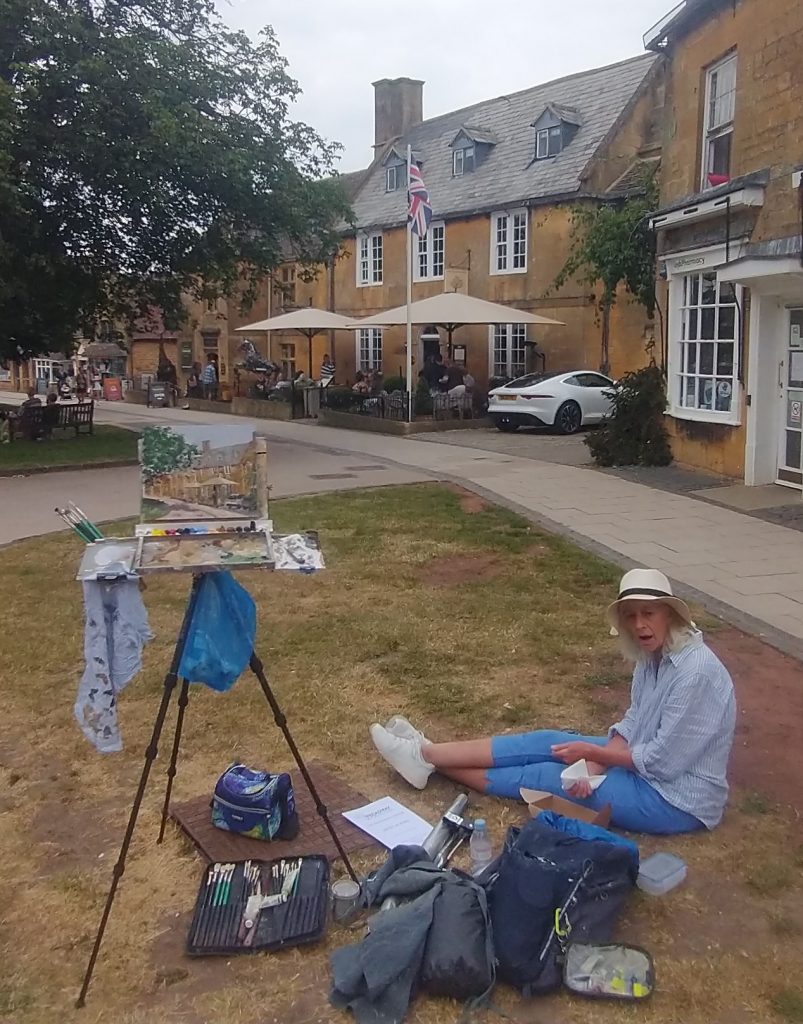
They take their blank canvases to create a work of art in the village. At 4pm or so, they are judged. At 5pm, the art works are exhibited and are on sale in the Marquee on the village green.
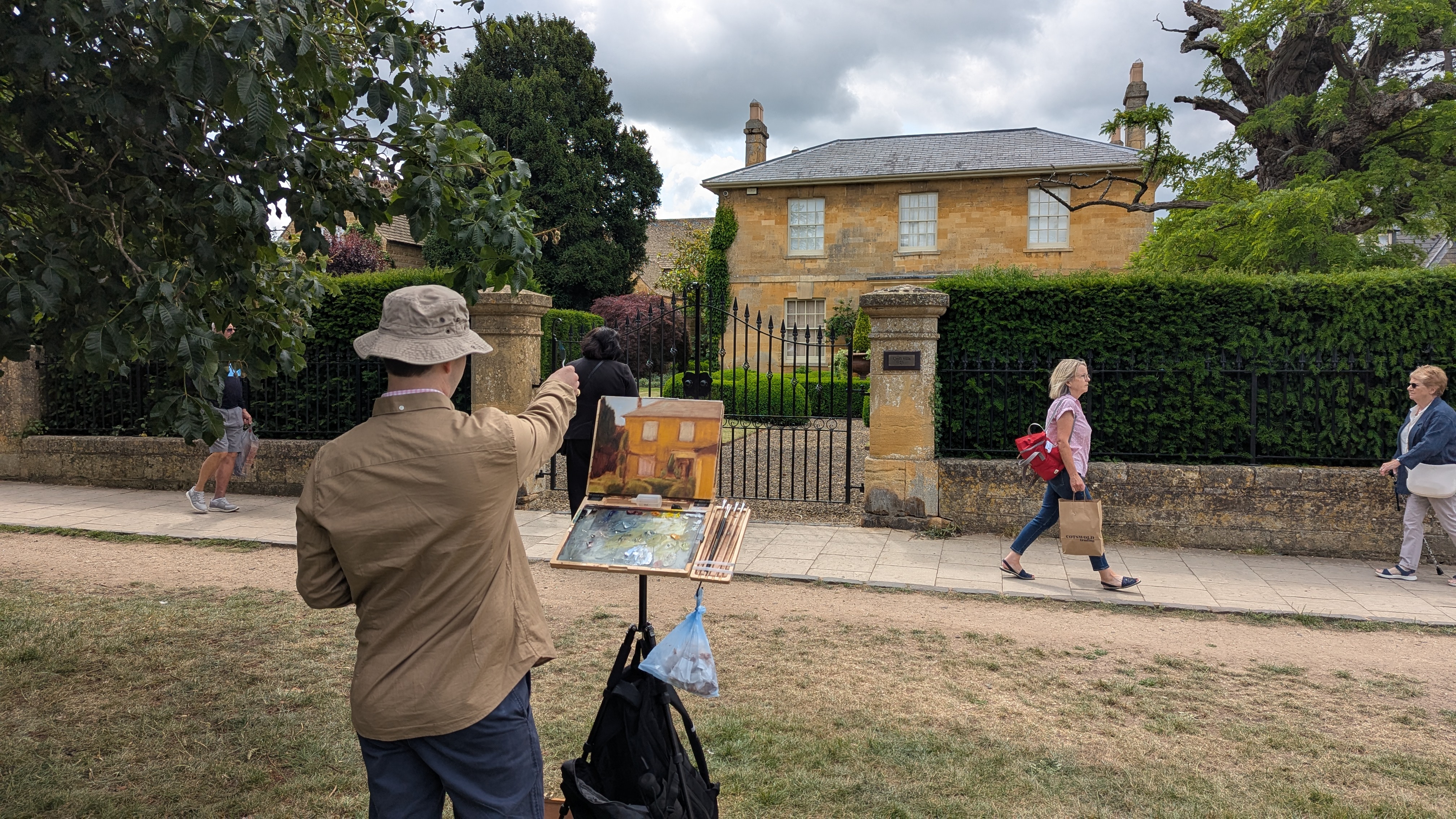

It’s always a delight walking around Broadway. Bun, but with an artist and easel every 50 yards or so even more enjoyable.
The Most Beautiful Village?
The appellation of most beautiful village, came in the late 19th Century. Broadway, once gained its wealth by selling wool. When that declined, the village became an important stop on the Toll Roads. It was on the stage coach route from Aberystwyth to Worcester, Oxford, and London. Fish Hill, nearly 1000 feet high, was an obstacle and coaches made a stop here to prepare or recover. Some coaches used up to 10 horses to get to the top. But with the arrival of Brunel’s Great Western Railway to the Cotswolds the village was nearly ruined. Half the village, the Broadway Museum says, moved away as their livelihood serving the coaching trade died.
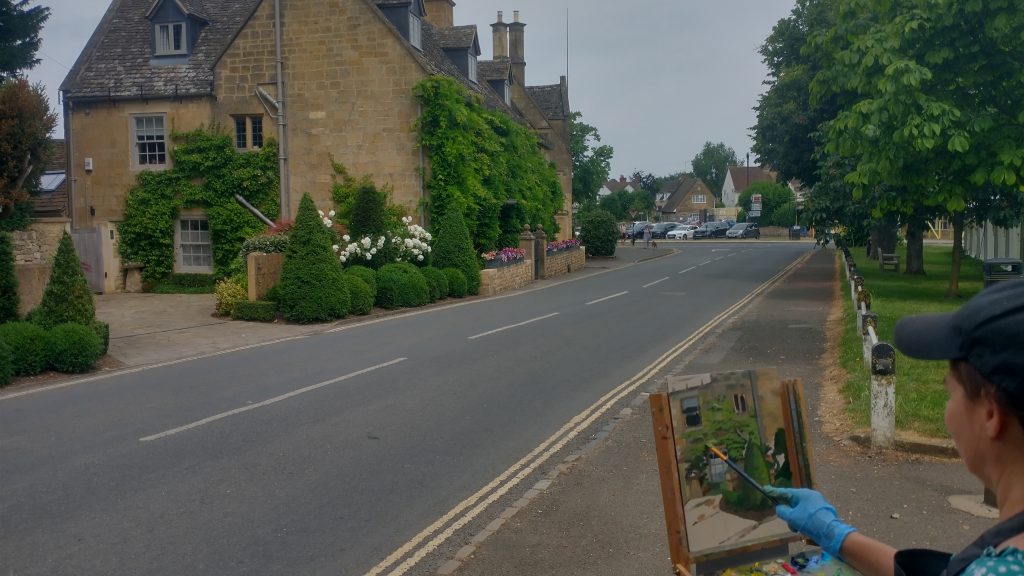
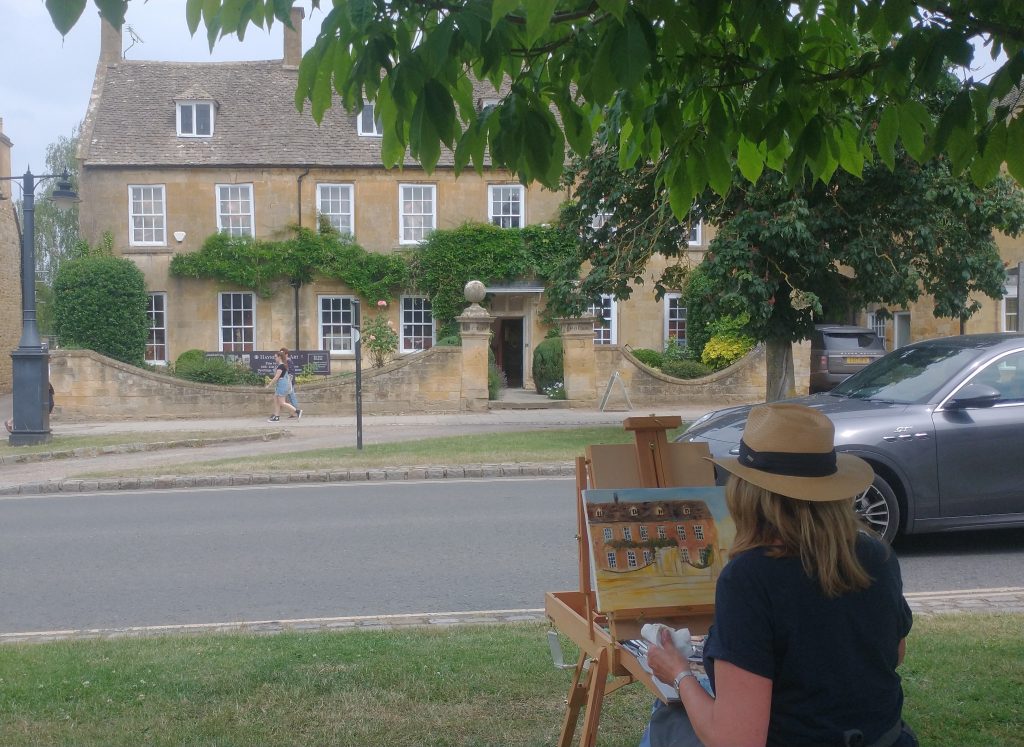



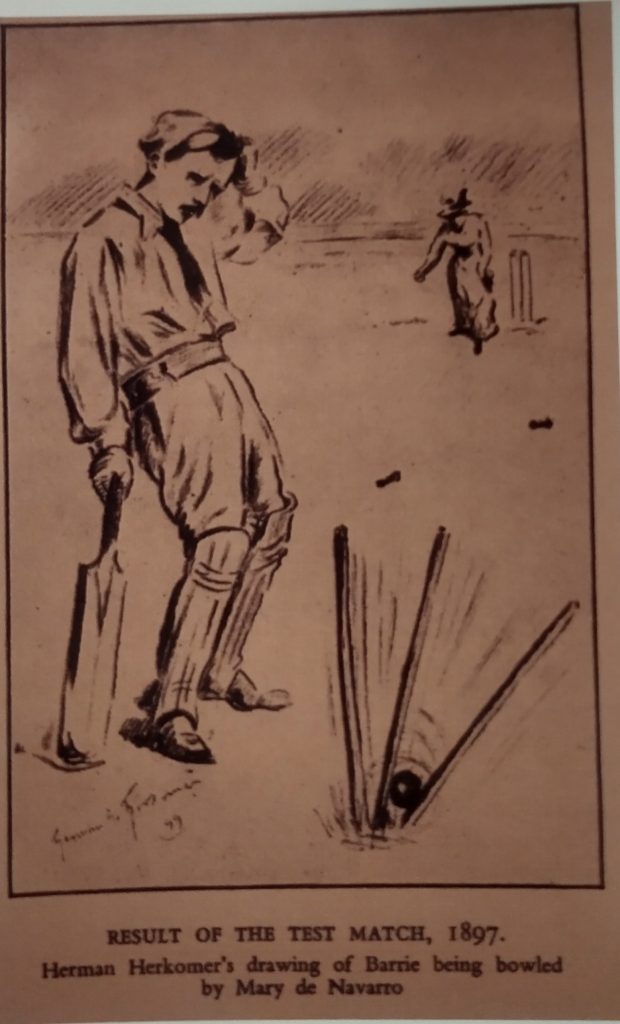
But artists and writers, led by Americans Frances Millet and Edwin Abbey, turned Broadway into a much sort-after country retreat. Visitors included Oscar Wilde, J. M. Barrie, Singer-Sargeant, William Morris, Edward Burne-Jones, Gabriel Dante Rossetti, American actress, Mary Anderson, Edward Elgar, E. F, Benson. Mark Twain visited for Millet’s marriage.

Gordon Russell & Henry T Ford
What made the visit particularly interesting was the story told by the volunteer at the Gordon Russell Museum in Broadway. This is the story as I understood it:
The Russells restored the Lygon Arms in Broadway using Arts And Crafts architects. They also restored antique furniture. The son, Gordon Russell, became a leading designer of modernist Furniture. He advertised to passengers on the Cunard Line in order to attract the attention of rich American visitors. One, Henry T Ford, was interested. He came to Broadway, staying at the Lygon arms. He was taken to nearby village Snowshill, where Ford bought a Cotswolds Farmhouse, complete with Blacksmith’s workshop. They were shipped stone by numbered stone to Brentford on the Thames. Then to the London Docks and across the Atlantic. Here. Ford set them up in a Museum in Michigan where they still are!

Research suggests it’s a little more complicated, in so far as Ford purchased his first Cottage before coming to Broadway. But it still leaves a delightful story about American ideas of Quintessential English village life. For pictures see my post here. And for another look at the story look at this web site here:
By the way, Frances Millet planned to return to the States on the Titanic. He was one of the 1500 who drowned. A letter he wrote while on the ship was posted, probably in France. It is on display in the Broadway Museum (2023).

For more about Broadway, Gordon Russell and Word War 2 see my post here:
June 18th is also:
National Chocolate Ice Cream Day
First Published in June 18th 2023, Republished in June 2024, and revised in 2025