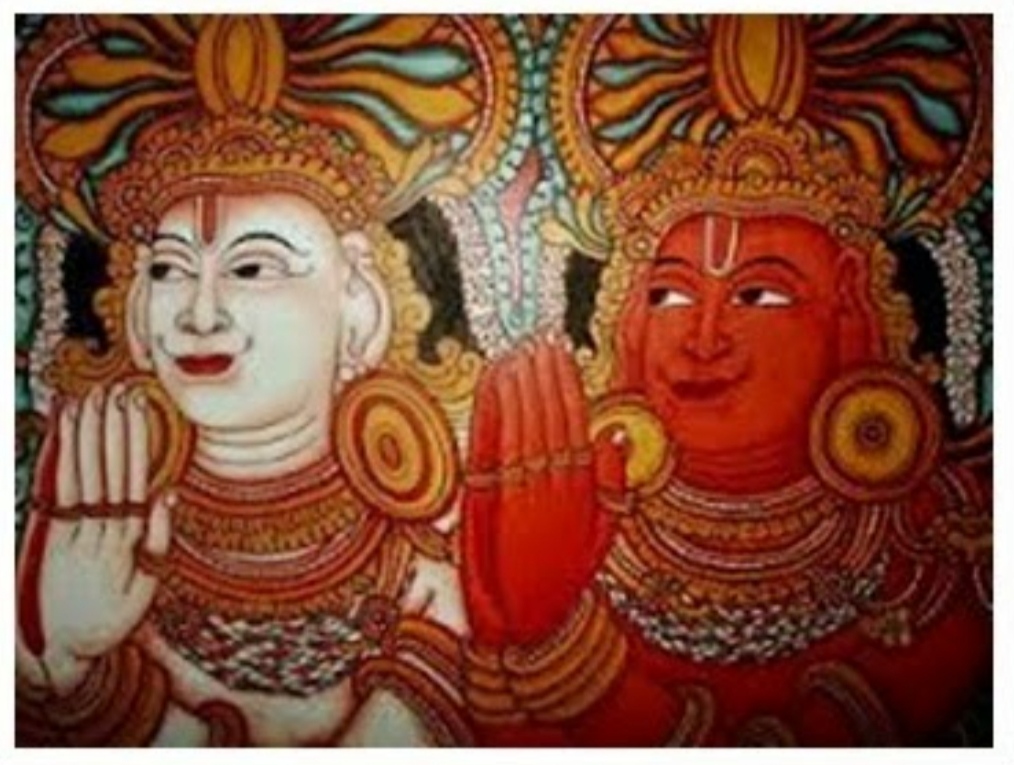
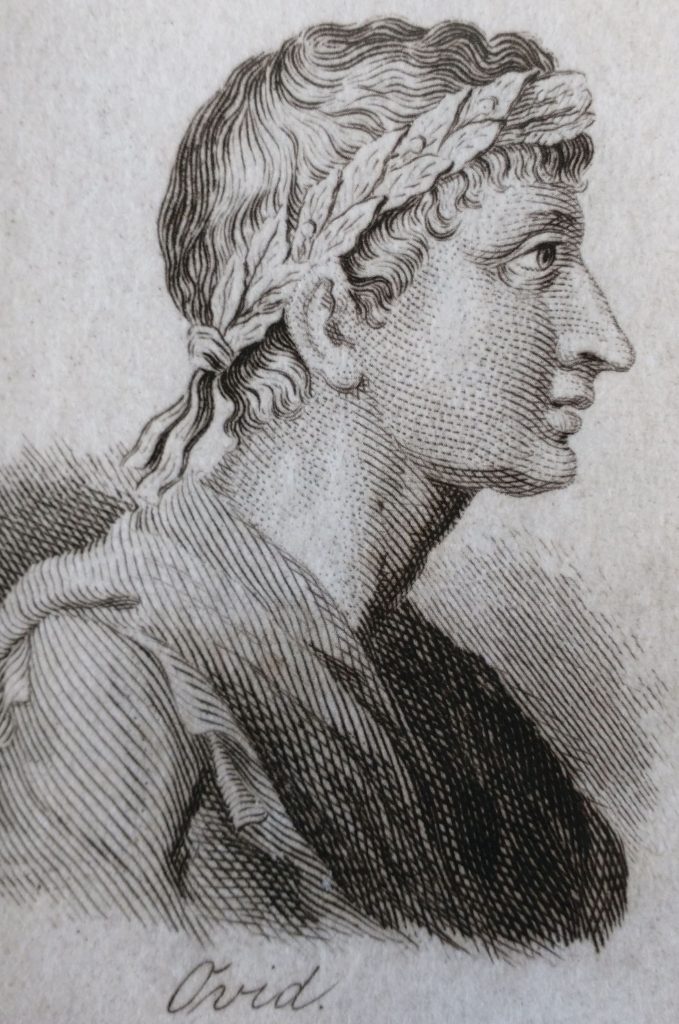
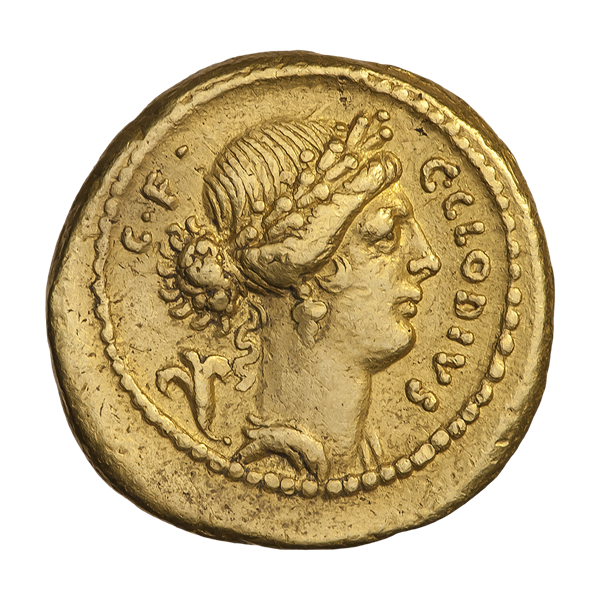
The Divine Twins, aka the Dioscuri, were horsemen, patrons of calvary, athletes and sailors, one of many indo-european twin gods. Pollux is the son of Zeus and Leda (raped by Zeus in the guise of a swan). His twin brother has a different and mortal father, the King of Sparta to the same mother, Leda. So they are examples of heteropaternal superfecundation as Mary Poppins probably didn’t sing.
One is therefore immortal and the other isn’t. They had many adventures including sailing with Jason as Argonauts.
According to some version of the story Castor was mortally wounded, and Zeus gave Pollux the option of letting his brother die while Pollux could spend eternity on Mount Olympus. The alternative was to share his immortality with his brother. He did the good thing, and the twins spend half their year as the Constellation of Gemini and the rest, immortal, on Mount Olympus. Thus, they are the epitome of brotherly love.
Their sisters were no less than Helen of Troy and Clytemnestra. They were also twins, Helen the divine daughter of Zeus and, Clytemnestra, mortal daughter of the King of Sparta.
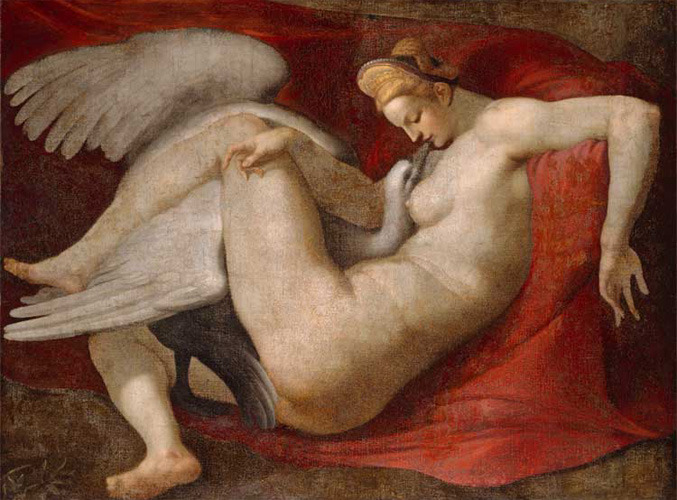
It happened like this. The Swan was being pursued by an eagle, so Leda protected the Swan and took it to bed. On the same night she slept with her husband Tyndareus of Sparta. Two eggs were fertilised, each split in two to give two sets of twins.

Never mind the Brothers, what Sisters! Helen you know. But Clytemnestra? She was the wife of Agamemnon, the arrogant leader of the Greeks. On the way to retrieve Helen from Troy, the Greek Fleet was becalmed. So, on advice, Agamemnon sacrificed his own daughter, Iphigenia, on the island of Aulis in exchange for a fair wind to Troy. (read Iphigenia at Aulis by Aeschylus, a great play which I studied in Classical Studies at University)

Meanwhile, Queen Clytemnestra, abandoned at home, broods on her husband’s heartless fillicide. She takes a lover. After 10 years of war, Agamemnon comes back, in triumph from the destruction of Troy, with his prize, the Trojan Princess, Cassandra. Strutting with arrogance, he demands Clytemnestra prepare him a bath, and, so she does, she gives him the hottest bath possible. With the help of her lover, she hacks Agamemnon to pieces with an axe.
Cassandra prophesizes that she too will be a victim. She has been gifted with the ability of accurate prophecy, albeit twinned with the inability to get anyone to believe her! She is also slaughtered.
I visit John Collier’s painting of Clytemnestra at the Guildhall regularly and am fascinated by her grim expression.
In the 18th/19th Century rich people were into ‘attitudes’. For example, Emma Hart, later Lady Hamilton, would be invited to present an attitude in front of a dinner party of mostly male aristocrats. She would dress up in a flowing revealing unstructured classical gown and stand on a table presenting herself as: Helen or Andromache or any other classical beauty guests might fancy an eyeful of. She would assume an appropriate facial expression and posture for everyone’s pleasure.

Being Clytemnestra is difficult! I imagine Collier’s model being prompted to look both sad at the loss of the daughter; outraged at the arrogance of the husband; horror at the gore of the murder but overall to portray a grim satisfaction that the bastard got exactly what he deserved.
Lord Leighton had a famous model who was exceptionally skilled at adopting poses for his paintings. He determined to help her with an acting career. As part of the plan he helped improve her cockney accent, and it is said this inspired Bernard Shaw’s story Pygmalion which, in turn, inspired My Fair Lady and Eliza Doolittle.
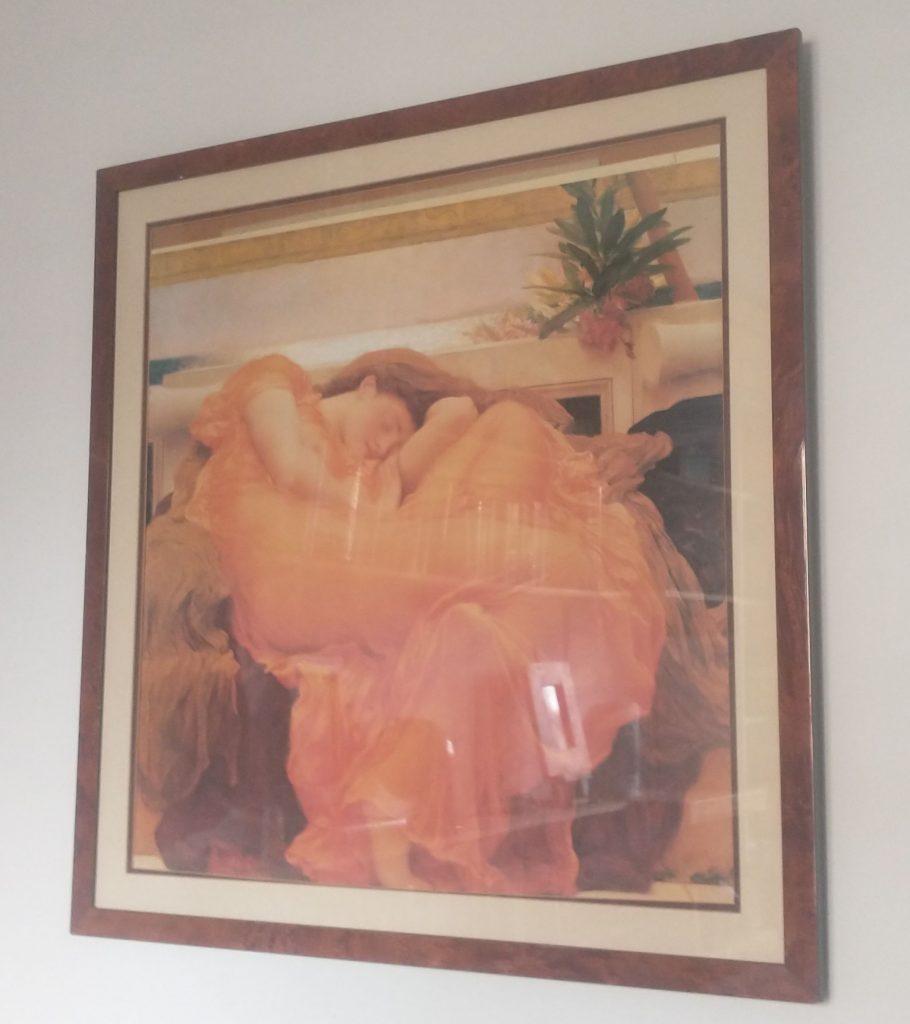
Leighton’s model was Dorothy Dene. She became a famous actress, outstripping the fame of Ellen Terry and Lily Langtry. She modelled for the famous painting ‘Flaming June’ which sold 500,000 print copies in 1895. Lord Leighton went somewhat out of fashion and the original painting was purchased for £50 by the rather marvellously named Museo de Ponce, Puerto Rico where she still resides.
I have one of those half million prints on my bedroom wall.

Before we finish, do have a look at John Collier’s Wikipedia because he is the most ridiculously well-connected painter you can imagine! Related to half the Cabinet and married to TWO daughters of Darwin’s Bulldog T.H.Huxley (grandfather of Aldous Huxley).
For more on Flaming June see my blog post of 12 July 2024
European Twin Gods
It is suggested that twin male gods are a feature of Indo-European religions, and that the Twins are associated with horses/chariots and are responsible for moving the Sun and the Moon. Their use of a horse above the water means that they can rescue people lost at sea. St Elmo’s fire was said to be the way they manifested their divinity to sailors. Diodorus Siculus records that the Twins were Argonauts with Heracles, Telamon, and Orpheus. Further, he tells us in the fourth book of Bibliotheca historica, that the Celts who dwelt along the ocean worshipped the Dioscuroi “more than the other gods”.
First written in 2023 updated in July 24.