Ovid says about the 16th February, ‘Next day is vacant.’ This is surprisingly encouraging to me because I have found it hard work finding something to say about some days. You can fill in with generalities, but the specific feels so much better. But. if Ovid can just say nought happened, then that is good enough for me. If you want to read Ovid’s almanac of the year, the ‘Fasti’, for yourself, this is the translation I am using.
Fasti is sadly unfinished because Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō was exiled by the Emperor Augustus when he was halfway through the Fasti. So the last entry is for 30th June where he says: ‘put the last touches to my undertaking’ suggesting he knew he was ending it here.
He was exiled until his death ten years later in Tomis, on the Black Sea. It is not clear exactly why he was exiled, ostensibly it was for the immorality in his book ‘The Art of Love’, but as that was published almost a decade earlier, it seems strange.
Was he involved with a plot against Augustus that saw the Emperor’s own daughter exiled? Her lover was Lullus Antonius, son of Mark Antony. Unlike Julia’s other lovers, he was forced to commit suicide.
But this also happened years before Ovid’s exile, so neither does it make any great sense of the great man’s punishing exile. However, Julia’s daughter was herself exiled closer to the time of Ovid’s exile and her husband, Lucius Aemilius Paullus, was executed for treason. Ovid said the reason for his exile was a ‘poem and a mistake’. The nature of that mistake is not recorded but he said the crime was worse than murder and more harmful than poetry.
Here is one of my favourite Ovid quotations. I quote from my own book which you can buy at the link at the bottom of the page.
‘Ovid, writing in Augustus’ reign, provides our guide to the flesh-pots of a Roman town. Here he recommends how the aspiring male should dress for a night out on the town:
Don’t torture your hair, though, with curling-iron: don’t pumice
Your legs into smoothness. Leave that
To Mother Cybele’s votaries, ululating in chorus
With their Phrygian modes. Real men
Shouldn’t primp their good looks …
… Keep pleasantly clean, take exercise, work up an outdoor
Tan; make quite sure that your toga fits
And doesn’t show spots; don’t lace your shoes too tightly,
Or ignore any rusty buckles, or slop
Around in too large a fitting. Don’t let some incompetent barber
Ruin you looks: both hair and beard demand
Expert attention. Keep your nails pared, and dirt-free;
Don’t let those long hairs sprout
In your nostrils, make sure your breath is never offensive.
Avoid the rank male stench
That wrinkles noses. Beyond this is for wanton women –
Or any half-man who wants to attract men.
Ovid, The Art of Love i
The translation is from Green, Peter (Trans) ‘Ovid The Erotic Poems’ Penguin Classics, London 1982‘
Mother Cybele’s votaries were castrati, hence their high pitched voices. Cybele fell in love with Attys, who made her jealous, so Cybele made him mad, whereupon he castrated himself and bled to death. The Mother Goddess had him resurrected body and soul and he enjoyed divine bliss ever after. A Cybelian castration device, dredged out of the Thames, can be seen in the Roman Gallery of the British Museum.’
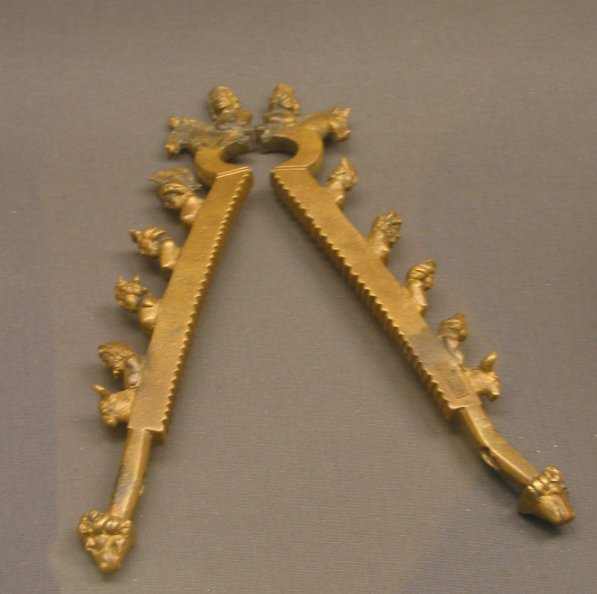

It’s quoted in In Their Own Words – A Literary Companion To The Origins Of London‘ D A Horizons, 2009. Kevin Flude
To buy Kindle version click here. To buy paperback (for £5.99) email kpflude AT anddidthosefeet.org.uk