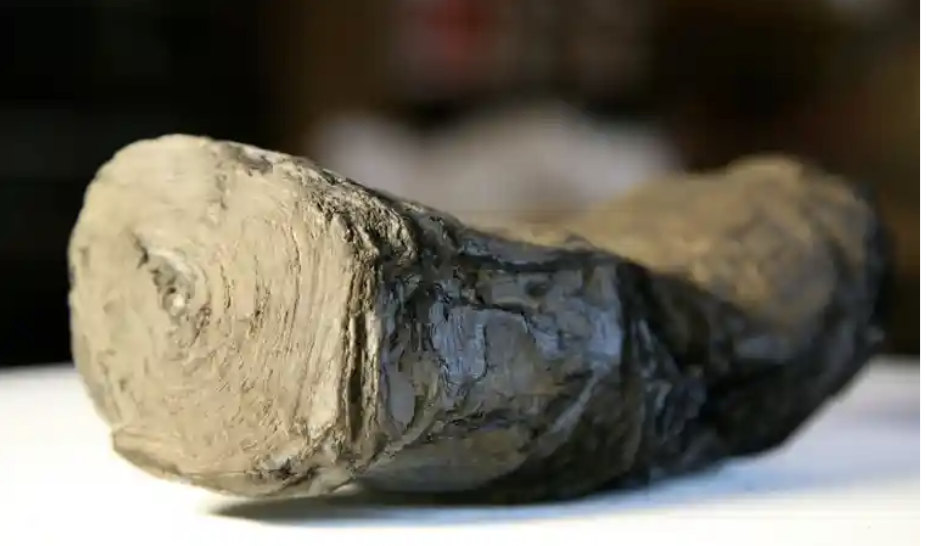
A study of the Stone of Destiny, the Stone of Scone, the Coronation Stone, has revealed new information. Firstly, it has some markings which look like three X’s and something like a V – perhaps Roman Numerals or more likely, crosses.
The Stone also revealed traces of copper alloy showing that a metal object had been attached to the Stone for a considerable time. The most obvious suggestion would be a relic associated with a Saint, and a Bell is one possibility.
Traces of gypsum suggested someone sometime made a plaster copy of the stone. No one knows when or why, and it has not been found.
Historic Environment, Scotland has released this fascinating 3-D scan of the stone for the public to view – it is annotated too.
You can read more at the links below, and thank you to Jean Kelly of the Britarch mailing list for alerting me to this.
Hidden symbols and ‘anomalies’ (Live Science)
Cutting-edge digital technologies (Historic Environment Scotland)
The Stone has been moved from its permanent home at Edinburgh Castle for the first time since 1996, to be placed under the Coronation Chair for Charles’s May 6 Coronation at Westminster Abbey.
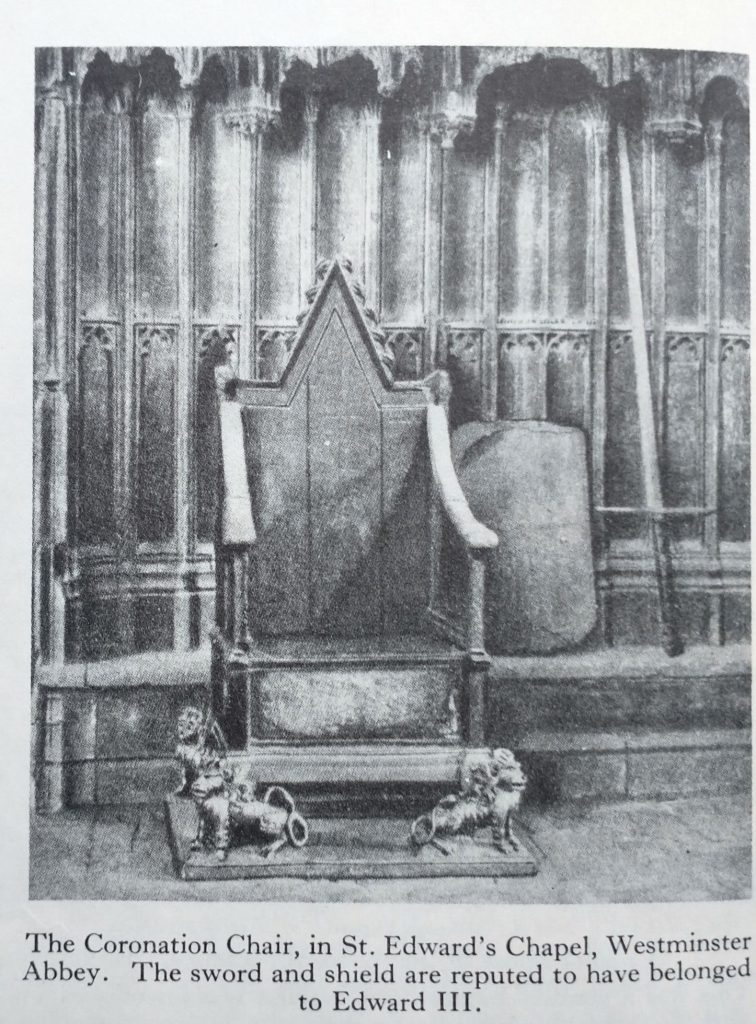
The Stone was kept at Scone before it was stolen by Edward 1 of England, who placed it under the Coronation Chair, at Westminster, to sanctify English Kings and to make the point that he was the overlord of the Scottish. In the 1950’s Scottish students stole it back, hid it for a few weeks and then left it at Arbroath Abbey. They did this because the so-called Declaration of Arbroath (1320) is a letter to the Pope asking for his endorsement of Scotland’s claim to be independent of England. The Pope agreed.
The Stone was recovered from Arbroath taken back to Westminster. The Labour Party under Tony Blair, granted Scotland back their own Parliament and as a symbol of their regained independence, the Stone of Destiny was taken back to Scotland.

To my mind it should be in Scone, which is where Macbeth and most other Scottish Kings were crowned, but perhaps they thought it should be in the Capital and in the safety of the Castle. At Scone, the Stone was placed on a mound of earth which was said to be made up of the dust from the feet of those attending Coronations symbolising the consent of all of Scotland for the new King.









