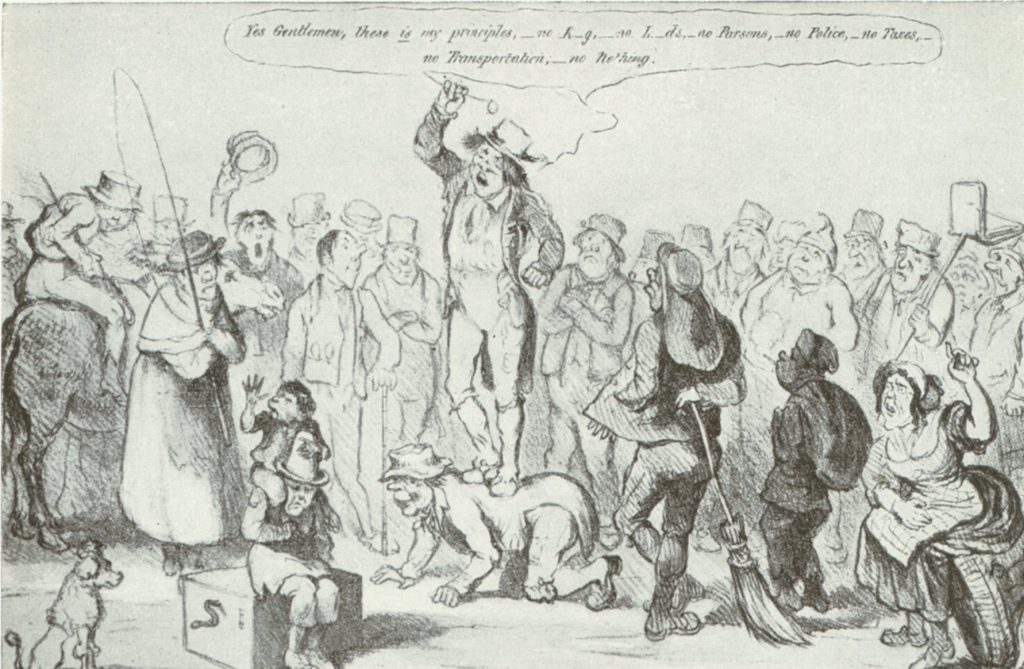
Socialists at St. Paul’s 28th February 1887
My French friend went yesterday to St. Paul’s and saw a large procession of socialists. It is a strange move of the socialists to visit all the Churches. The Archdeacon of London preached to them from: “the rich and poor meet together, and the Lord is the maker of them all.” A noble sermon, they behaved fairly well.
Helen G. McKenney, Diary, 1887 (source: A London Year. Compiled by Travis Eldborough and Nick Bennison)
The quotation is from the Bible, Proverbs 22, where it sits with a number of other wise sayings. Perhaps, number 16 ‘One who oppresses the poor to increase his wealth and one who gives gifts to the rich—both come to poverty‘ is most likely to stir a Socialist, but generally, I imagine the Archdeacon was also making a point that the Lord made the Rich and the Poor, so there is nothing wrong with being Rich, as long as you are generous to the Poor, and equally, nothing wrong with being Poor.
It’s rather lovely to imagine the Socialists walking around Wren’s masterpieces in the City of London. However, later in 1887, things turned much worse, when the Social Democratic Federation and the Irish National League organised a march against Unemployment and the Irish Coercion Acts. The Police had been trying to prevent the ever-increasing use of Trafalgar Square as a protest venue. So, on November 13th, Bloody Sunday, the Police Commissioner, Charles Warren, ordered a massive police presence backed up with 400 Soldiers. His aim was to prevent the entry to Hyde Park. Among the 10 to 30 thousand citizens presence were William Morris, Annie Besant , George Bernard Shaw and Eleanor Marx.
By the end of the day there were 2 people dead, 100 seriously injured, 45 arrests, 75 accusations of police brutality and many Police Casualties. Warren had already resigned following criticism of the failure to find Jack the Ripper, but was acting as a caretaker until the new Commissioner was in place.

Before the Foundation of the Labour Party, progressive politics were in the lukewarm hands of the Liberal Party, which developed from the Restoration period Whig Party. The Liberal Party had a radical wing, but it had a reluctance to put forward working-class candidates. In the early 19th Century, much of the agitation was led by the Chartists, but as their goals became adopted by the main two parties, progressive politics was led by various reform, radical, socialist, marxist and anarchic groups.
I have not been able to find out who led the 1887 City Churches Socialist walk, but because of William Morris’ membership, I am wondering whether it was the Socialist League? In 1885, the Socialist League was an offshoot of the Social Democratic Federation. But it was not a harmonious group. Its most famous members were William Morris, and Eleanor Marx. It included Fabians, Christian Socialists and Anarchists. By 1887 it was split ideologically into three main factions, Anarchists, parliamentary orientated Socialists, and anti-parliamentary Socialists. William Morris was the editor of their newspaper, ‘the Commonweal’ but he was sacked and replaced by Frank Kitz as the Anarchists took over the organisation.
So, without going into a long history of Socialism in London, what happened was that the Socialist groups made very little impact until the Independent Labour Party was set up in Bradford 1893. And in 1900, Keir Hardie, who was already an independent MP in Parliament, set up the Labour Representation Committee in 1900, which was soon renamed the Labour Party. The Independent Labour Party joined and Labour began to take over control of the working-class vote. It fought the Liberal Party for the progressive vote, but it was not until after World War 1, with the decline of the Liberal Vote that it was able to secure minority Governments and not until after World War 2 that it replaced the Liberals as one of the two Political Parties which could win a majority in Parliament.
London was one of the places where the Party experimented with policies that led to the National Health Service, particularly in the East End areas of Poplar, Limehouse and Bermondsey.
My Grandma who was born in Petticoat Lane in 1902, voted for Labour all her life. I’m pretty sure it was out of class loyalty because I always thought her opinions were not typical of Labour voters.