
Feralia is the last day of Parentalia a 9-Day Festival for the spirits of the Dead described in some detail by the Roman Poet, Ovid, in his Almanac of the year called the ‘Fasti’. Here, he describes how to honour a parent:
And the grave must be honoured. Appease your father’s
Spirits, and bring little gifts to the tombs you built.
Their shades ask little, piety they prefer to costly
Offerings: no greedy deities haunt the Stygian depths.
A tile wreathed round with garlands offered is enough,
A scattering of meal, and a few grains of salt,
And bread soaked in wine, and loose violets:
Set them on a brick left in the middle of the path.
Not that I veto larger gifts, but these please the shades:
Add prayers and proper words to the fixed fires.
There is much more Ovid says about Feralia, and you can read it for free, in translation by A. S. Kline (which I used above, at www.poetryintranslation.com)
For more about Parentalia look at my earlier post about the February festivals of the Romans:
In London, archaeologists have found many cemeteries around the City of London. The Romans forbade burial inside the City limits, so the dead were buried alongside the main roads out of the City Gates: Aldgate, Bishopsgate, Holborn, along Fleet Street, outside Ludgate, and along the main road South from London Bridge in Southwark.
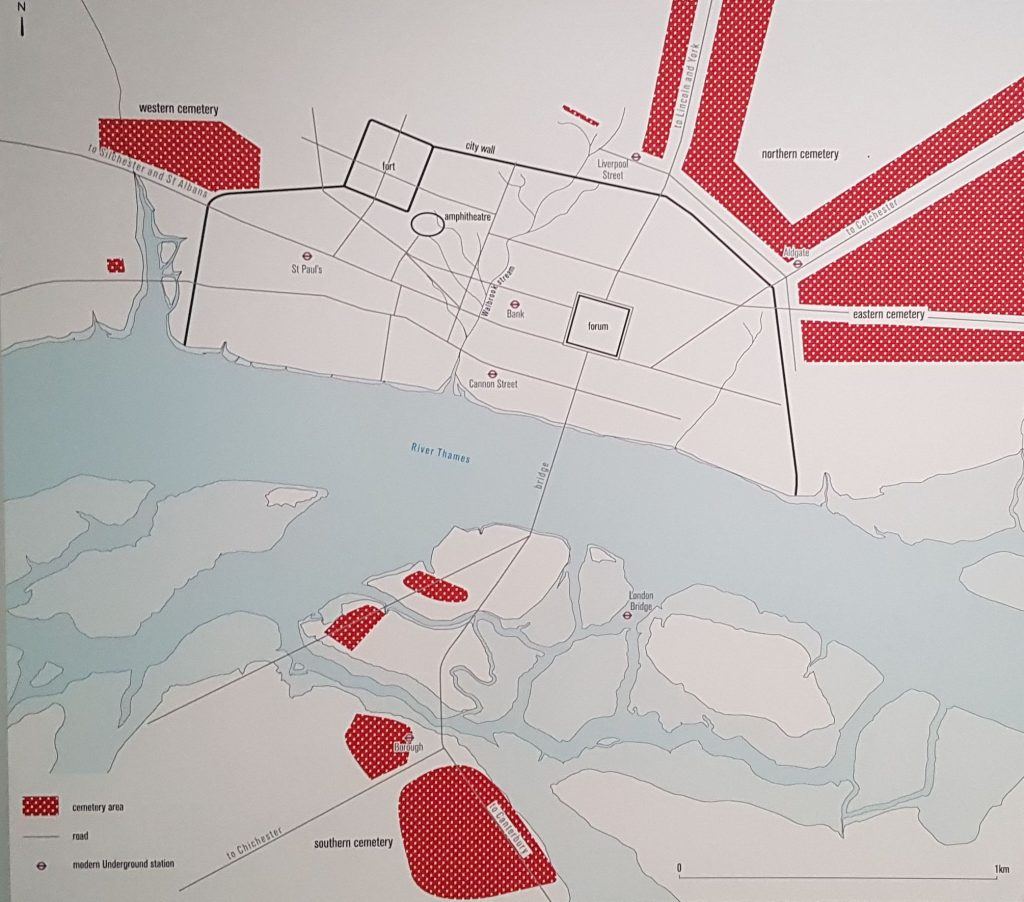
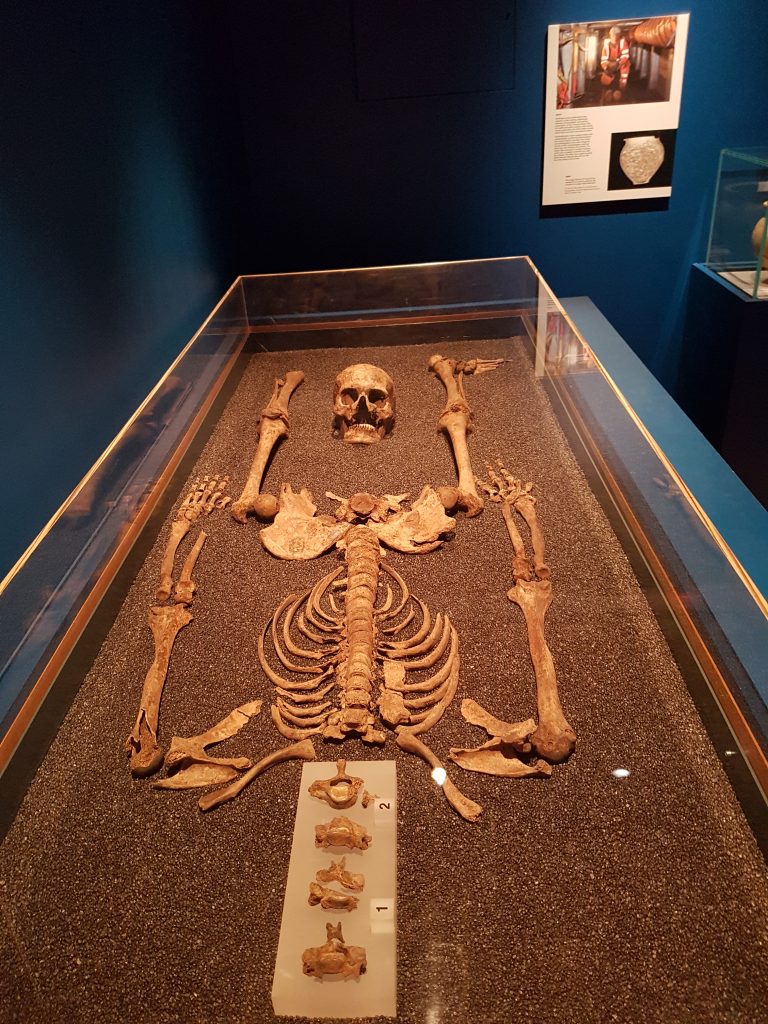
Various rites have been observed. Both inhumation and cremation practised. I remember excavating a Roman mortaria with a hole in the bottom with the ashes of the dead in it. These large bowls were used as a mortar for grinding foodstuffs. The bottom was deliberated gritted, but they often wore through, and sometimes found reused to hold cremation ashes. I like to imagine, granny being buried in her favourite cooking vessel (or grandad).
Many bodies were covered in chalk, perhaps to help preserve the body. A surprising number of bodies are found with the head by the knees. The large number of cases helps speculation that this was a burial rite, of whom only a percentage were beheaded as a punishment. Some graves shown signs of a funeral pyre.

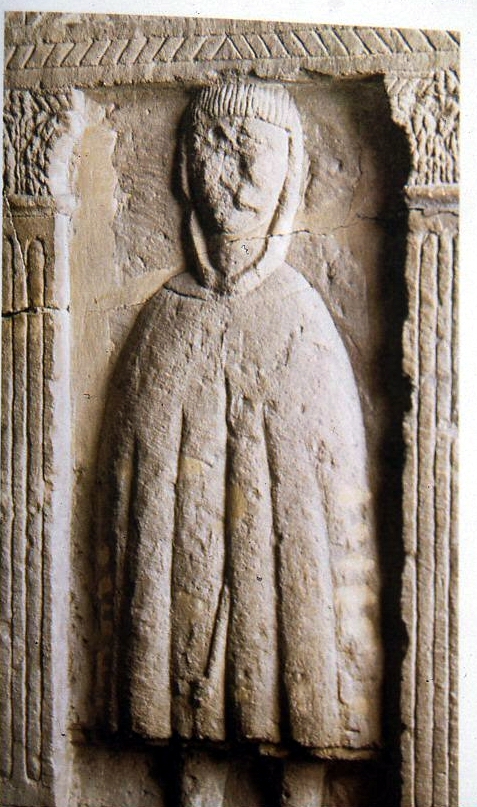
The rich and powerful were remembered with huge monuments, prominently sited along the main roads. Perhaps the most famous are the burial stones found at Tower Hill of the Procurator Classicianus. This is famous as he is mentioned in Roman accounts of the Boudiccan Revolt of AD 60-61. He suggested to Nero that the Province could only be saved if the revenge against the British was de-escalated. Nero wisely withdrew the vengeful Roman Governor Suetonius Paulinus and replaced him with someone ready to conciliate. We, clearly, have lessons to learn from the Romans.

A beautiful carved eagle which adorned a tombstone was found in the Cemetery in Tower Hamlets. But recently a very grand mausoleum was found in Southwark. To find out more, have a look at the BBC website here:
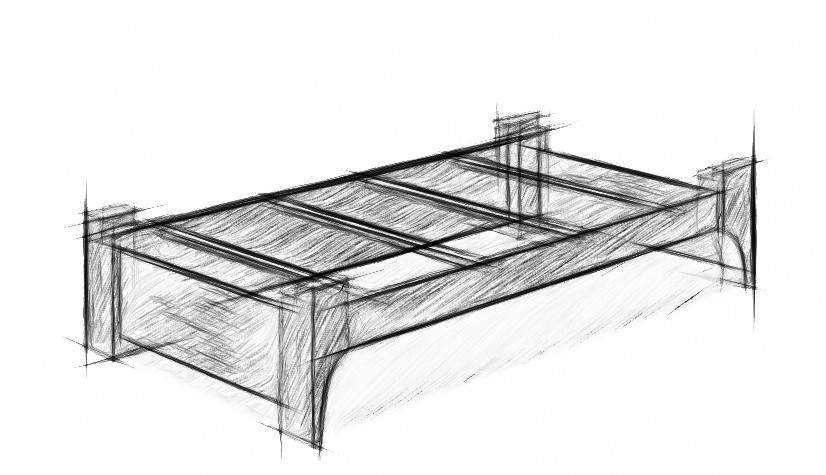
Finally, a week or two ago, an excavation ran by MOLA discovered a ‘funerary bed’ in an just outside Newgate in Holborn. It was on the banks of the River Fleet, a tributary to the River Thames, that gives its name to the street of shame: Fleet Street. The fluvial location meant that there were extraordinary levels of preservation, which included this bed. It was dismantled and buried in the grave and may have been either/or or both a bed used as a grave good, perhaps for use in the hereafter, or the bed upon which the deceased was carried to the funeral.
They found other grave goods, including an olive oil lamp decorated with an image of a gladiator; jet and amber beads and a glass phial.
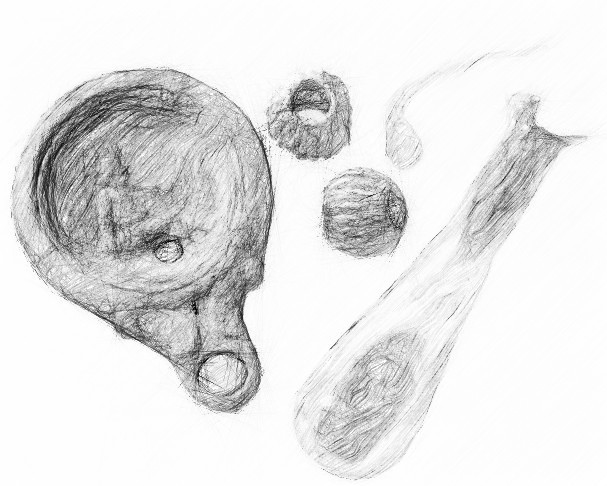
For more look at www.mola.org.uk/discoveries
Discover more from And Did Those Feet
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
