St Artemios is the patron saint of male genital disorders, more specifically, hernias and ruptures. His Saint’s Day is October 20th St. Artemios was Governor of Egypt during the reign of Julian the Apostate (331 – 26 June 363). Julian was a philosopher. nephew to Constantine the Great, who tried to turn the tide and return to traditional Roman religious practices. Artemios was called to a military meeting with Julian where he witnessed and objected to abuse of Christians. He was tortured with red hot irons, and miraculously cured. Then he was taken to the Amphitheatre where there was a big stone broken in half, and was put on half stone and the other half was raised above him and released crushing Artemios. He was presumed dead, and left for a day. But he was still alive, broken boned, disembowelled, eyeless and remained unwilling to renounce his religion and Julian ordered his beheading.
A noble woman took his body to Constantinople where his shrine soon started attracting miracles. In the 7th Century an anonymous author compiled a record of the miracles. St Artemios had become known for healing hernias and genital disorders ‘mostly in men.’ I’m not sure entirely why. Perhaps because of the red-hot pokers? The disembowelling? Maybe the stone that crushed was round?
I first came across the Saint when my mother-in-law bought me a wonderful book called ‘A Medieval Miscellany selected by Judith Herrin and with an introduction by the great Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie (see Jan 27th Post to read about Montaillou and Ladurie). It had a colourful spread called ‘The Miracle of the Testicles’ which was the story told by Stephen, a 7th Century deacon of St. Sophia in Constantinople who ‘suffered a rupture, whether from shouting acclamations or from a heavy weight, I cannot say.’
To cut a long story short, Stephen was very embarrassed by his condition and eventually tried many cures and finally undertook surgery, which was successful but very soon the condition reoccurred which left him to despair.

So he planned to visit the shrine of the great healer of testicles, but was too embarrassed to stand in the Church ashamed to be seen by friends. But passing by one day he nipped into the Tomb, descended to where the relics were and ‘cast’ some of the Saint’s holy oil on his testicles. He then found, much to his surprise, that the doors to the Coffin itself were open. Seeing this as a divine intervention he jumped onto the coffin, straddled it face down, so that the corner of the tomb was rubbing his testicles and prayed:
‘And with tears, I spoke again to the martyr: “St.Artemios, by God, Who has given you the gift of cures, no doctor on Earth will ever touch me again. So if you please, cure me. But if not, to your everlasting shame I will live thus without cure.‘
He was not cured immediately. Later he went to the Hot Baths and bathed, and on leaving the baths, thanks be to St Artemios, he was completely cured.
I have transcribed the translation of Stephen’s writings and place it here below as it has many fascinating aspects and remember it is a 7th Century account. But what an extraordinary tale: that it seems reasonable to steal into a tomb, take the holy oil, rub your genitals all over the shrine, and then tell the Saint that it will be to his everlasting shame if he does not make the cure!
For more on the Hospital of Sampson click here. Livanon is one of the Roman Baths in Constantinople and it is interesting that the cure follows bathing in them. The Oxeia is a neighbourhood in Constantinople connected with St Antemios. A cautery is a method to remove or close off a part of the body. It can be hot, cold or chemical.
At long last I disclosed the misfortune to my parents, and after many treatments, (how many!) had been performed on me. Finally, after taking counsel with them, I entrusted myself for surgery to the surgeons in the hospital Sampson, and I reclined in the hospital room near to the entrance to the area devoted to eyes.
After I had been treated all over for three days at night with cold cauteries, surgery was performed on the fourth day. I will omit to what horrible things I experienced while on my back.
To sum up everything, I state that I actually despaired of life itself at the hands of the physicians. After God, entreated by the tears of my parents, restored my life to me, and after the scar from the incision and the cautery had healed, and just as I was believing that I was healthy, a short time later, the same condition recurred and so I reverted to my former state…
I had a plan to approach the holy martyr, as I had heard of his many great miracles. Still, I was unwilling to wait in the venerable church feeling ashamed before friends and acquaintances to be seen by them in such condition. But I frequently used to pass by (for at that time, I was staying in the Oxeia). And so I descended to the holy tomb of his precious relics, and I cast some of his holy blessing, I. e. oil on my testicles, hoping to procure a cure in this manner. And frequently, I entreated him to deliver me from the troublesome condition…
After descending to the holy tomb, I found the doors in front open and I was astounded that they were opened at such an hour. This was the doing of the martyr, in his desire to pity me, Stretching out facedown on the holy coffin, I straddled it, and thus contrived to rub the corner of the same Holy tomb on the spot where I was ailing. And with tears, I spoke again to the martyr: “St.Artemios, by God, Who has given you the gift of cures, no doctor on earth will ever touch me again. So if you please, cure me. But if not, to your everlasting shame I will live thus without cure.’ And after some days I went to the bath in the court of Anthemios, the one called Livanon to bathe by myself at dawn in order not to be seen by anyone . And entering the hot chamber, I noticed that I still had the injury. But upon exiting, I had no injury, and recognising the act of kindness on the part of God and the martyr which is befallen me… in thanksgiving… I do now glorify them proclaiming their deeds of greatness throughout my whole life.
From Medieval Miscellany selected by Judith Herrin Pg 54 the Miracle of the Testicles
Originally, published on February 13th 2023 Revised, and republished October 20th 2024
On the 23rd of February 2023 I opened this post with the following:
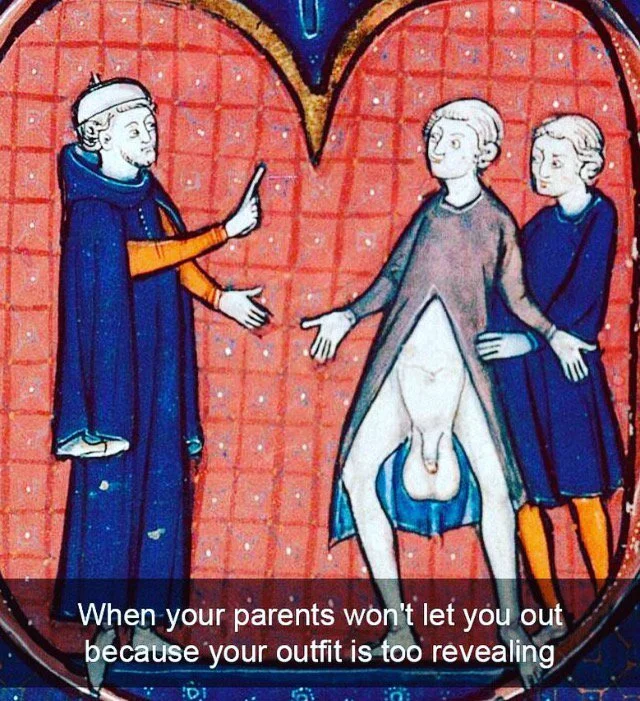
I hope you will forgive me for raising this subject early because of personal circumstances.
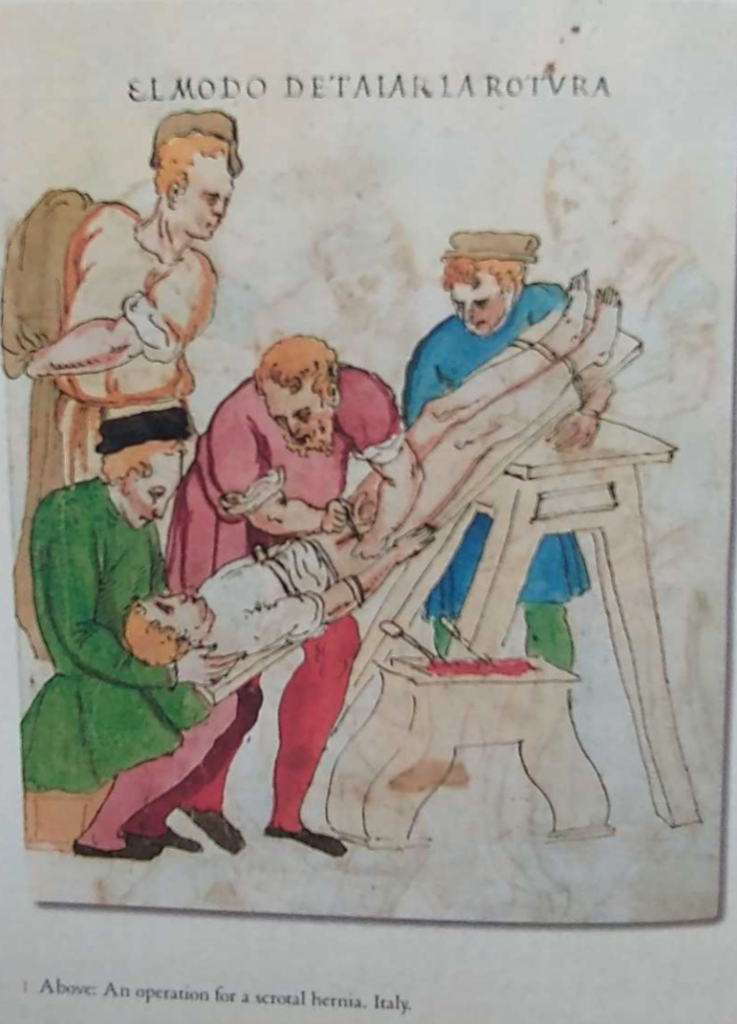
Yesterday, I did a Chaucer’s London Virtual Tour – one I first prepared during the dark days of Covid. As I was revising the presentation, I was surprised to discover that I had illustrated a piece on medieval health care (St Thomas Hospital, Chaucer’s Physician) with images of medieval hernia operations. Surprised, because I am currently recovering from an inguinal hernia operation and suffering a little so that the image (above) which, coincidently, popped up in facebook made me laugh. Obviously, I was meant to write about testicles today.