I was puzzled to find a message, from reader of this blog Harriet Salisbury, voicing interest in coming on my ‘Decline and Fall of Roman London’ Walk in order to find out about Roman Dental problems.
Harriet is not only a brilliant editor, but also the author of a great book on the oral history of war time London, so I had to follow up this puzzling comment. And my recent post on my upcoming walk said:
Faced with plaque, civil war, invasion, mass immigration, industrial decline, reversion to barter; the authorities struggled against anarchy and descent into a Dark Age
Now there are many reasons for the decline and fall of the Roman Empire but I have never yet heard anyone, apart from me, blame dental plaque. So, I then spent a couple of hours changing the q of plaque to the g of plague in various places where the deadly dental disease was referred to. Of course, Harriet might equally have wondered whether a rash of information panels had been a contributory cause?
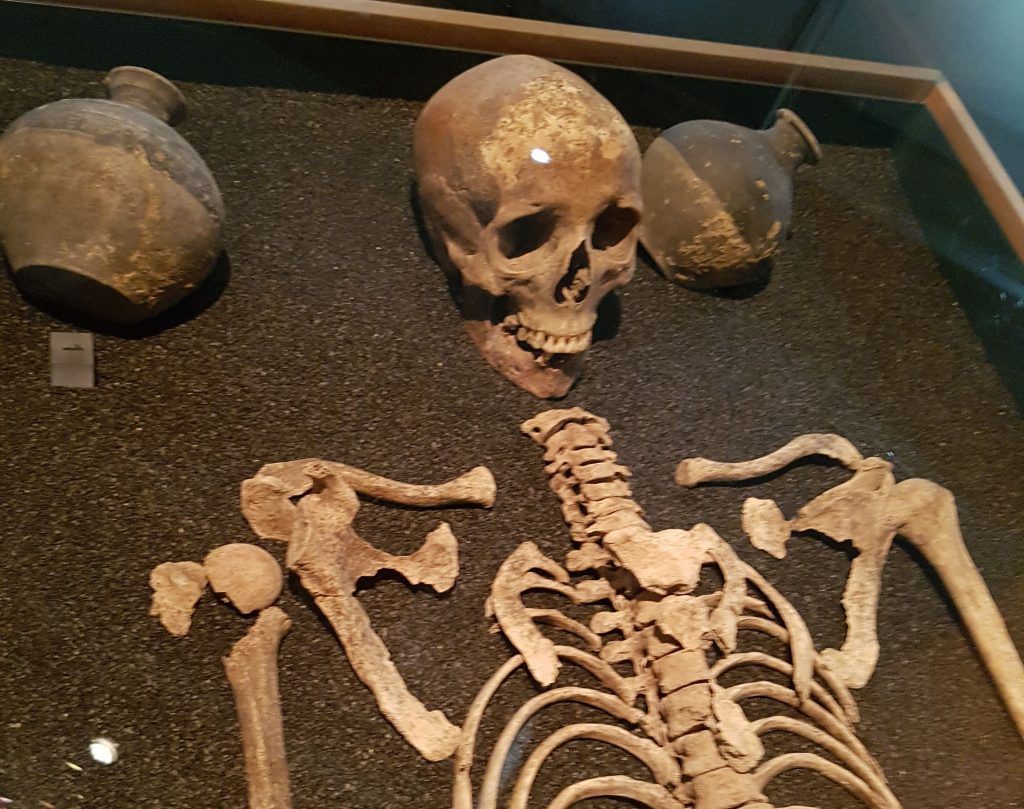
As you will know I have an interest in the history of health and medicine. A cursory glance at any of the skeletons you find in museums will normally show that pre-modern skulls have much better teeth health than modern people. And the reason for this is, mostly, because they did not have sugar to rot their teeth. Instead of sugar-created cavities, their problem tended to be wearing teeth out by the roughness of the grain they used. But I investigated more and found that recent work in Herculaneum and Pompeii had investigated Roman teeth health in a scientific manner. This showed that the diet of even the poor was much better than most modern diets because it was essential the much lauded ‘Mediterranean Diet’ with olive oil, no added sugar, lots of vegetables,fruits and smaller amounts of meat. In short, Roman society had a system in which even the poor had balanced nutritional diets, and therefore good levels of natural immunity.
Pompeii also had a high level of fluoride in the water. The Romans seem to have brushed their teeth with a flayed stick and used abrasives made of ‘ground-up hooves, pumice, eggshells, seashells, and ashes‘. They used a mouth wash of human and animal urine, and disgusting as this may seem, the ammonia would have acted as a cleansing agent.
To find out more about the science behind the story please go to: https://www.docseducation.com/blog/ancient-romans-had-healthier-smiles-we-do-today
This picture from ebay shows you a flayed stick toothbrush – I include the seller information so you can buy some!
Harriet’s book was based on a wonderful oral history collection at the Museum of London. Worth having in you are interested in London history, the Blitz and ordinary people’s lives. And also for any lover of ‘Call the Midwife’.

I have updated and reposted my January 4th post to include what to look out for in the night skies in January.





