As Christmas looms, seasonal publications have a mixture of wonder and joy at the coming family reunions and festivities mingled with an awareness that, for some, Christmas will depend on the Food Bank or the Charity Shelter. The weather is now cold, living costs continue to rise at the very time extra spending is needed to unlock the joy of the Season, and to counter the dark, the cold and the spectre of death which, in fact, has always been central to the season of winter.
Charles Dickens’ Christmas Books epitomise this dichotomy and adding an element of the supernatural, provided a vehicle for joy and hope, but with a forceful political message that the authorities and the rich were not doing their Christian duty to alleviate poverty. Christmas Carol contrasts the wealth of a mean rich Stockbroker with the family of his poor employee Bob Cratchit, and provides a powerful tale of redemption.
But in this post I want to concentrate on his second Christmas Book, ‘The Chimes’. It tells the story of the stick-thin Trotty Veck who is an aged City messenger, nicknamed Trotty because of his habit of keeping himself warm by running on the spot. He is afraid to let his daughter, Meg, to marry as he has so little hope for the future. While he is worrying, he, Meg and her intended Richard are approached by Alderman Cute and Mr Filer.
Cute represents the financial industries in the City of London and the Law. Filer the new breed of political economists. These, working with the idea of Malthus and the new science of Statistics, had proved, that generous support for the poor would, inevitably, lead to a country full of poor people and no rich people. And thus, they justified the Poor Law Amendment Act of 1832 which Dickens observed as a Parliamentary reporter (1831-1834). This set up the cruel Workhouse system which provided the lowest possible level of support offering separation from family, meagre food, and sparse comforts to encourage them to stop being lazy and get back out there to earn their own living and allow taxes to fall. (brilliantly satirised by Dickens’ Oliver Twist, asking for ‘More’).
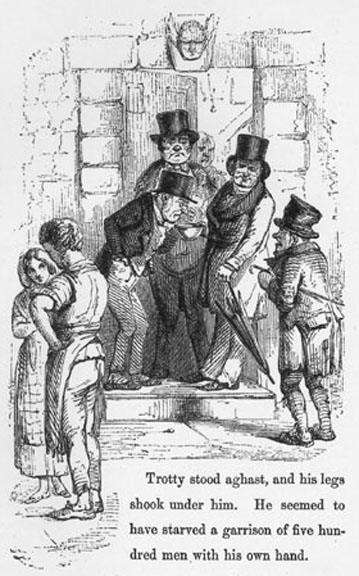
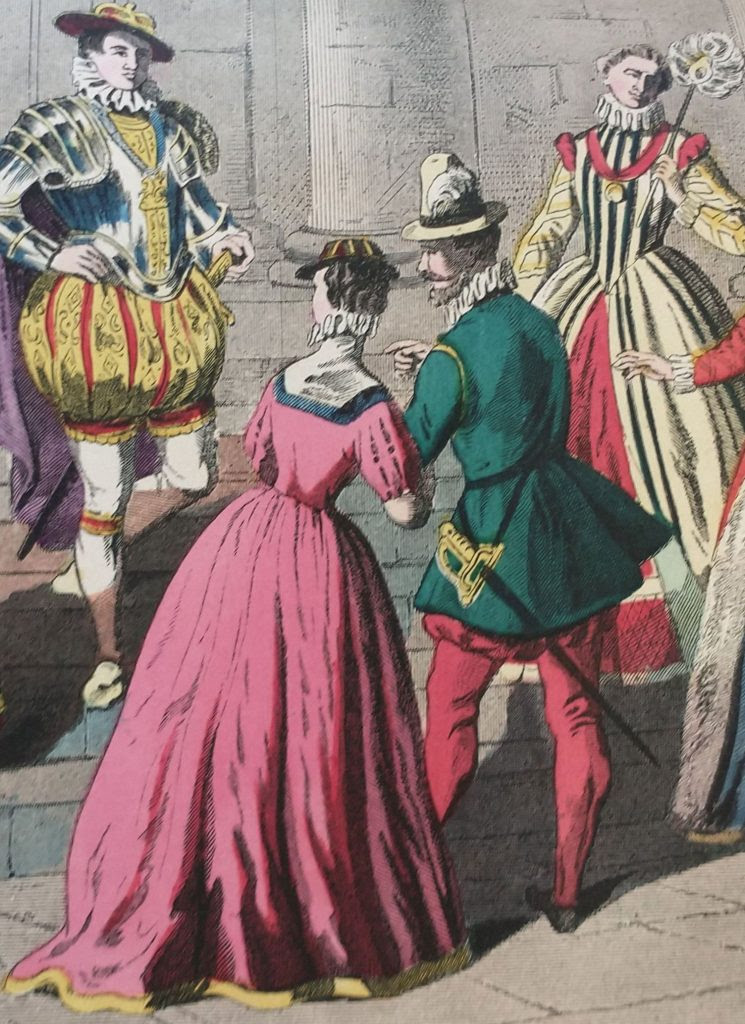
Below, I enclose the scene from the Chimes, which satirises the attitude of the governing classes.
‘And you’re making love to her, are you?’ said Cute to the young smith. ‘Yes,’ returned Richard quickly, for he was nettled by the question. ‘And we are going to be married on New Year’s Day.’ ‘What do you mean!’ cried Filer sharply?Enough ‘Married!’ ‘Why, yes, we’re thinking of it, Master,’ said Richard. ‘We’re rather in a hurry, you see, in case it should be Put Down first.’ ‘Ah!’ cried Filer, with a groan. ‘Put that down indeed, Alderman, and you’ll do something. Married! Married!! The ignorance of the first principles of political economy on the part of these people; their improvidence; their wickedness; is, by Heavens! enough to—Now look at that couple, will you!’ ... ‘A man may live to be as old as Methuselah,’ said Mr. Filer, ‘and may labour all his life for the benefit of such people as those; and may heap up facts on figures, facts on figures, facts on figures, mountains high and dry; and he can no more hope to persuade ’em that they have no right or business to be married, than he can hope to persuade ’em that they have no earthly right or business to be born. And that we know they haven’t. We reduced it to a mathematical certainty long ago!’ Alderman Cute was mightily diverted, and laid his right forefinger on the side of his nose, as much as to say to both his friends, ‘Observe me, will you! Keep your eye on the practical man!’—and called Meg to him. ... ‘Now, I’m going to give you a word or two of good advice, my girl,’ said the Alderman, in his nice easy way. ‘It’s my place to give advice, you know, because I’m a Justice. ... ‘You are going to be married, you say,’ pursued the Alderman. ‘Very unbecoming and indelicate in one of your sex! But never mind that. After you are married, you’ll quarrel with your husband and come to be a distressed wife. You may think not; but you will, because I tell you so. Now, I give you fair warning, that I have made up my mind to Put distressed wives Down. So, don’t be brought before me. You’ll have children—boys. Those boys will grow up bad, of course, and run wild in the streets, without shoes and stockings. Mind, my young friend! I’ll convict ’em summarily, every one, for I am determined to Put boys without shoes and stockings, Down. Perhaps your husband will die young (most likely) and leave you with a baby. Then you’ll be turned out of doors, and wander up and down the streets. Now, don’t wander near me, my dear, for I am resolved, to Put all wandering mothers Down. All young mothers,of all sorts and kinds, it’s my determination to Put Down. Don’t think to plead illness as an excuse with me; or babies as an excuse with me; for all sick persons and young children (I hope you know the church-service, but I’m afraid not) I am determined to Put Down. And if you attempt, desperately, and ungratefully, and impiously, and fraudulently attempt, to drown yourself, or hang yourself, I’ll have no pity for you, for I have made up my mind to Put all suicide Down! If there is one thing,’ said the Alderman, with his self-satisfied smile, ‘on which I can be said to have made up my mind more than on another, it is to Put suicide Down. So don’t try it on. That’s the phrase, isn’t it? Ha, ha! now we understand each other.’ Project Gutenberg - The Chimes by Charles Dickens
It is a savage burlesque of a satire but at its core. Filer provides the economic/statistical justification. Cute enforces it by legal harassment of the poor. Dickens was writing after a recent introduction of legislation making suicide a punishable offence.
This has a contemporary resonance. During my lifetime the first British Government to be cruel in its provision, in my opinion, for the poor was Teresa May’s Conservative Government. Her laws made getting help so difficult that people died as a result of the deliberately difficult system. ‘I, Daniel Blake’ a 2016 film by Ken Loach brilliantly captured the essence of this system. That government’s treatment of the Windrush generation was a similar example of bureaucratic cruelty. And the continuing decline of the benefit system over the 13 years of Conservative Government means that the poor have borne the brunt of austerity.
The piece above reminds us what a brilliant propagandist Dickens was. Every generation of children, since he wrote Christmas Carol, has read it or seen it in popular retellings such as The Muppet Movie. I think it could be argued that the ‘More’ scene in Oliver Twist and the Christmas Carol have made the case for compassionate care and redemption far beter than contemporary Christianity or political parties.
In the Chimes. those two men discourage Trotty from letting the young ones marry. He has a dream and sees the hopeless result of his decision: suicide, prostitution, crime. When he wakes up, he realises that what they do have is hope. Hope springs eternal and he lets them marry.
For more on this scene, have a look at the Victorian Web
Dickens was not a socialist. ‘Hard Times’ shows that Dickens was against strikes, despite leading a strike when he was a young newspaper man. He was a free trade Liberal; a reformer who believed that the rich needed to do their Christian duty and provide charitable support, pay decent wages and look after their dependents and servants. He thought society should care less about the dogma of Christianity but look to its essence, ‘love your neighbour like yourself’. This, alone, was sufficient to right the wrongs caused by the selfish.
First Published on December 16th 2022, republished and revised in December 2023.