Folklore is full of ways of predicting the future – mostly about the weather or love. The Perpetual Almanac by Charles Kightly features many of these in rhyme form of the ‘Sky at Night Shepherd’s Delight’ type. Here is a seasonal one.
If ducks do slide at Hallowentide
At Christmas they will swim
If ducks do swim at Hallowentide
At Christmas they will slide
From my experience, in the south of the UK, this is simply not true as we very rarely get ice in early November, and don’t get snow at Christmas that often. But maybe, the further north you go, the truer this becomes. But it’s good to remember what Macbeth said on seeing the wood moving to Dunsinane ‘(I) begin to doubt the equivocation of the fiend, that lies like truth.’ as he realises that prophecy is a double-edged sword which has led him to his doom. He had been told by the Three Witches that he:
‘shall never vanquish’d be until Great Birnam Wood to high Dunsinane Hill shall come against him’
Still, as he heads to the final battle, Macbeth knows he is invincible and that ‘none of woman born shall harm Macbeth’.
But in his savage fight with Macduff, he is told that Macduff was not of woman born, but rather ‘from his mother’s womb / Untimely ripped’. And Macbeth is killed.
In reality Macbeth, was a successful King who reigned for 17 years, and was one of the last Gaelic Kings as Scottish society was changing with contact with England.
This is a draft of the text that forms part of my best-selling book ‘Divorced, Beheaded, Died’ The Kings and Queens of Britain in Bite-sized Chunks’
King Macbeth (Mac Bethad mac Findlaích) 1040 – 1057
Macbeth was nicknamed the Red King. He was a Gaelic speaker, descended from the Kings of Dal Riata. Macbeth’s father, Finlay MacRory, was Mormaer (Grand Steward) of Moray. He was murdered by Gillacomgain, who took MacRory’s title. Gillacomgain was burnt to death with 50 of his followers, probably by Macbeth, who thus not only regained the title as ruler of Moray but married his dead rival’s widow, Gruoch. She was the granddaughter of Kenneth II. Macbeth was also himself descended from the Kings of Scotland via his mother Donada probably daughter of Malcolm II.
His claim to the throne was therefore strong, and following the disasters of King Duncan’s reign, Macbeth seized the opportunity to take the throne for himself.
He ruled well for nearly 2 decades imposing a strong sense of law and order, encouraging Christianity and leading successful raids across the border into England. In 1050 he went on pilgrimage to Rome. Exiled Normans, supporters of Edward the Confessor were settled in Scotland in Macbeth’s reign. There is no evidence that Macbeth was any more evil then the rest of the early Scottish Kings.
In 1057 Macbeth was killed in battle against Duncan I’s son who became Malcolm III. Macbeth is buried on Iona. He and Gruoch had no children but Guoch’s son, Lulach, son of Gillacomgain briefly followed Macbeth as king before being assassinated by Malcolm III
‘Divorced, Beheaded, Died’ The Kings and Queens of Britain in Bite-sized Chunks’ for more details look here.
Prophecy ‘lies like the truth’ a trope that is used in many ancient tales such as Oedipus Rex.
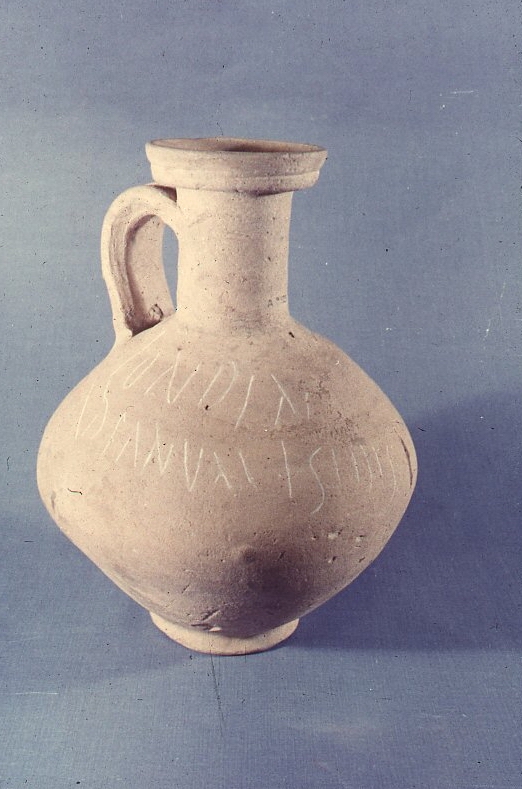
The 3rd of November is the Hilaria, the last day of the festival of Isis/Osiris, the day of the rebirth of Osiris. Isis was the wife (and brother) of Osiris God-King of Egypt who was killed by his brother. Isis restored his body to life for long enough to conceive their son Horus, who revenged his father, regained the throne, restored Cosmic Order and completed the resurrection of Osiris. Isis is normally shown holding the baby Horus in a pose that may have influenced images of the Virgin Mary. Londinium would have had a celebration on this day as there is a pot found near London Bridge inscribed ‘At London, at the Temple of Isis).

Also on this day
St Winifred’s Day She was beheaded by Caradog who would not take her refusal to have him because of her religious views. She was restored to life by St Beuno, or St Bono.

First Posted on 3 November 2021. Revised 3 November 2023 & 2024 & 2025