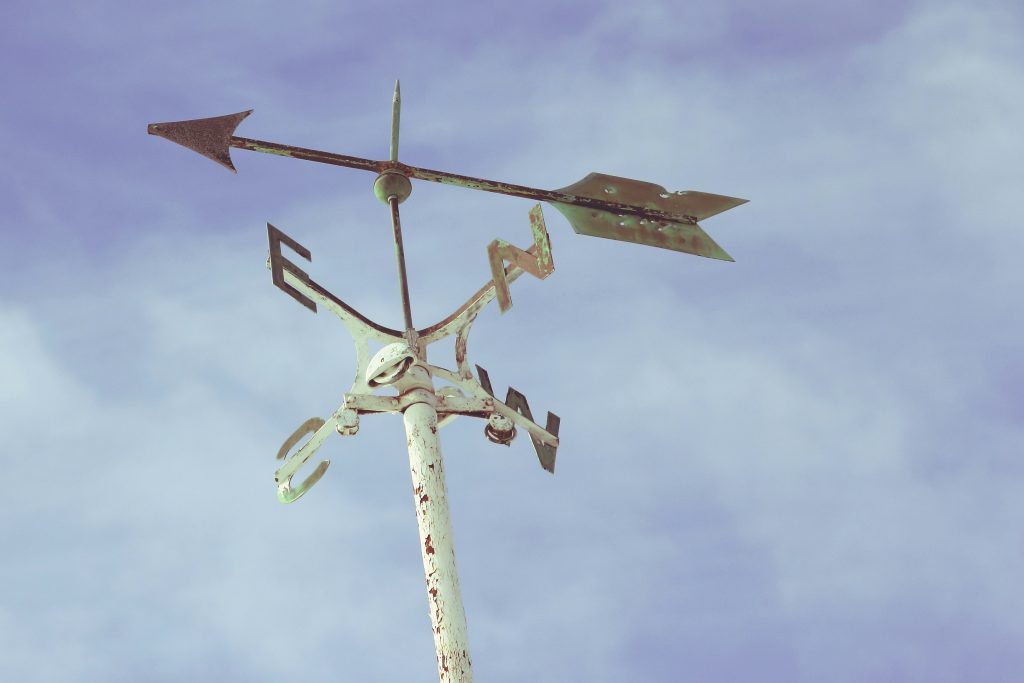
The day after the Equinox we look at the cardinal points of the compass:
“chief, pivotal,” early 14c., from Latin cardinalis “principal, chief, essential,” (online etymological dictionary).
The Importance of South
On its annual cycle, the Sun is always on the move. At the Equinox the Sun now rises due East, and sets due West. It then rises every day further towards the north and sets further to the South until the Solstice. The Solstices mark the extreme Northerly and Southerly rising and settings. Dawn and Dusk vary accordingly.
So, the only real fixed point in the Sun’s entire journey (as seen from Earth) is Noon. Every day of the year, every day of our lives, the Sun is at the highest point at Noon. And this is the definition of South. But the Sun never strays into the North. So the North is the polar opposite of the South- cold, remote, more mysterious, unknowable almost.
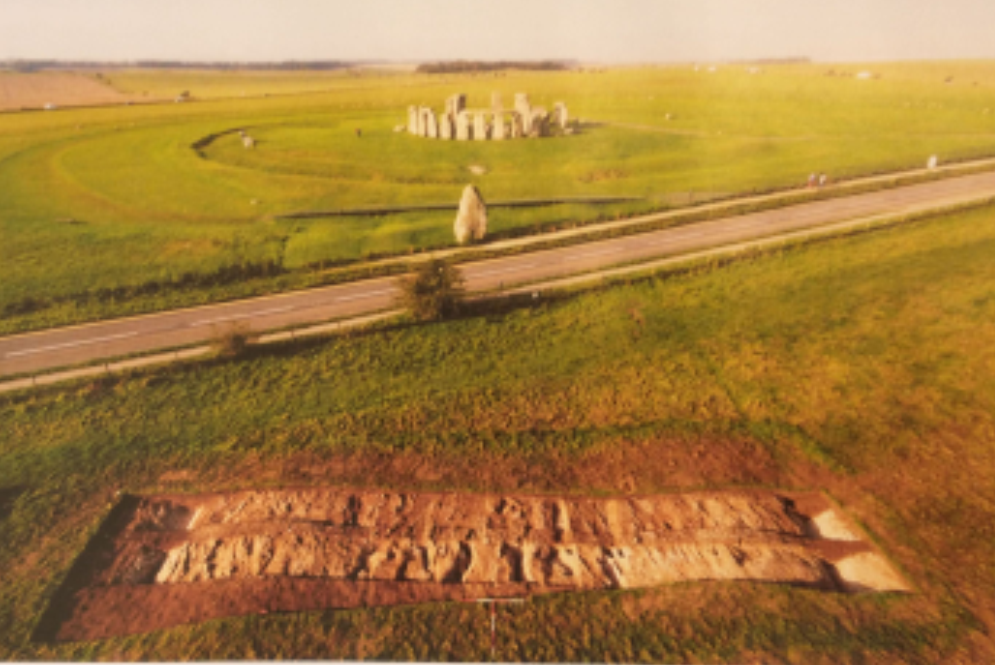
To my mind, it makes, of the Cardinal Points, the South very special. At Stonehenge, there are two exits. The biggest is aligned to the Midsummer Sunrise and Midwinter Sunset axis. But there is a smaller second entrance and this aligned due South. There is also a uniquely small standing stone in the main circle of Sarsens, which is aligned to the South. (Although we don’t know if this stone is original). However, there was some sort of corridor heading South through the mysterious wooden phase which precedent the stone Stonehenge. So, we can be fairly sure South was important at Stonehenge.

Noon, derives from ‘nona hora’ in Latin and is ‘one of the seven fixed prayer times in traditional Christian denominations.’ (Wikipedia)
The Predominance of the North?
And yet, North, has come to be the principal of the cardinal points. It is shown on virtually all modern maps. It is the direction that people of my generation and hemisphere think of as being ‘up’.
The Google generation sees things differently. There are countless tourist maps on walls or plinths where North is no longer at the top. Up is shown as being the way you are facing. Users have to fight with Google Maps to put North at the top of the map. My children mock me when I say ‘Out of the Tube station, turn up the High street northwards.’ Their view of maps is completely contextual. They do not see any reason to know where the cardinal points are. I point out that the Tube probably has two exits on either side of the road. So, it doesn’t work to say ‘turn left out of the tube’.
There may also be an element of sexual difference, with men more likely to have a cardinal point view while women navigate more by landmarks. ‘Walk past the M&S, turn left to the Park and straight on’. One paper says: ‘during spatial navigation, women typically navigate an environment using a landmark strategy, whereas men typically use an orientation strategy.’
Although I see this decline of the north as being part of the Decline of the West. I also ‘things were better in my day’. But in fact it is simply returning to the way maps were produced in the past. Here is an example below.
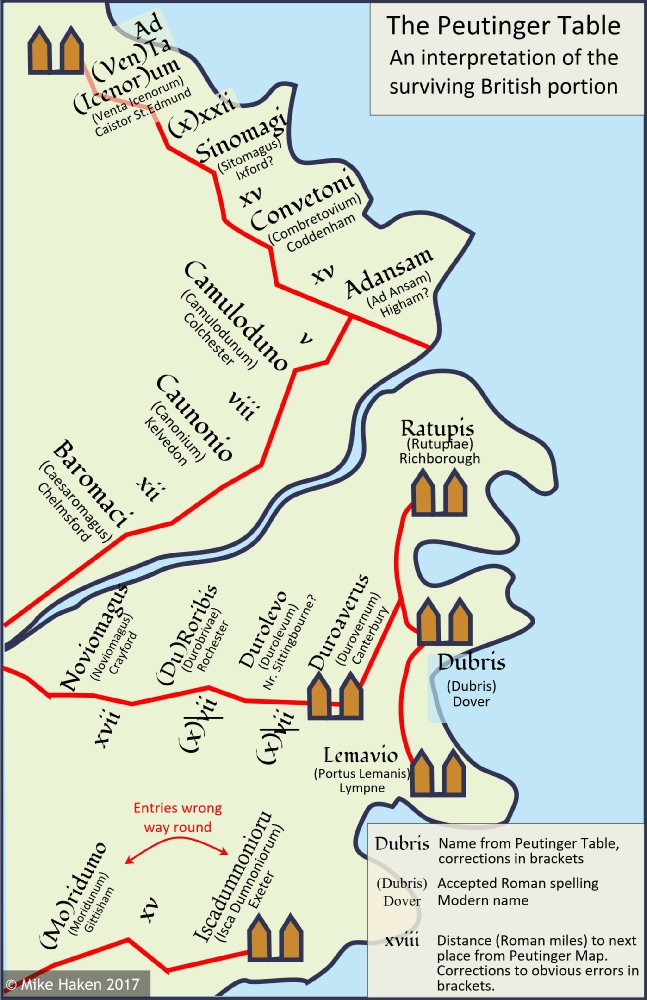
The Magnetic Poles
Of course, there is another version of the cardinal points: the magnetic cardinal points. The magnetic North wanders over time. It does not necessarily coincide with geographic north. In recent times they are close enough. But in the past there have been huge variations. Occasionally, the earth has had geomagnetic reversals when the North Pole has pointed in different directions, including south. The last one was 780,000 years ago. On average, they take place very roughly every 500,000 years.
The magnetic pole is caused by the molten iron in the earth’s core and mantle, which creates a dipole. Fluctuations in the dynamo flow of the molten iron cause occasional reverses. The science is very complicated and, even now, not entirely understood. Is it a random consequence of flow dynamics? Or do external events, like sinking continents, or meteor strikes cause the reversal?
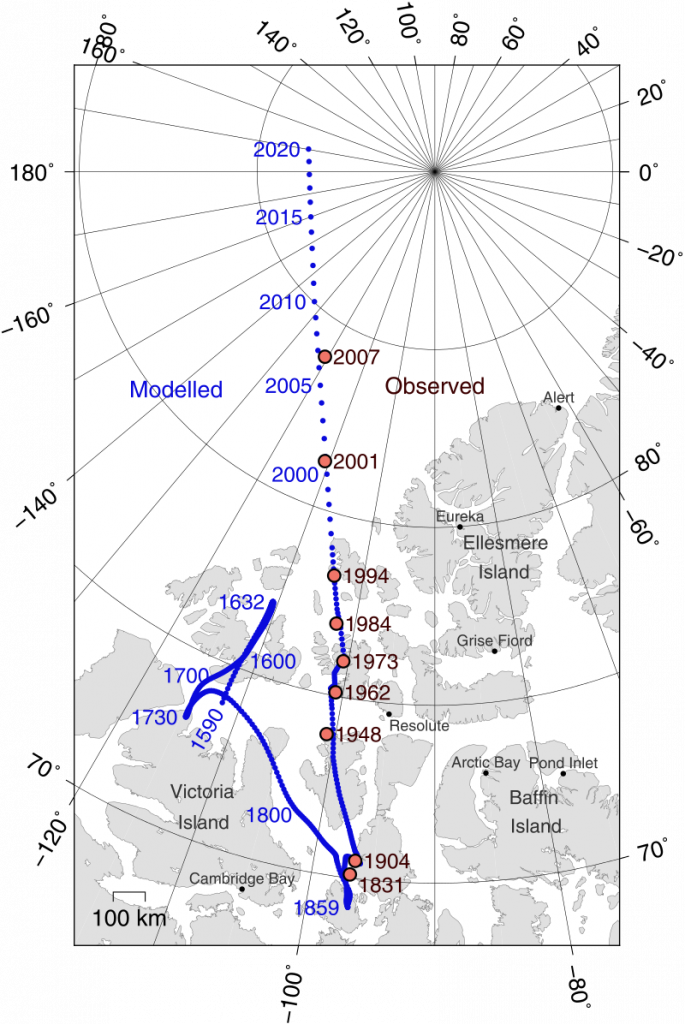
Since the first use of compasses for navigation in the 11th/12th Centuries, the magnetic pole hasn’t wandered enough to be of concern to navigation. It has wondered a few hundred miles over the last 500 years. Now, it is speeding up, from 9km a year to 52km (since 1970). This Wikipedia page is pretty good at an explanation.
My Job Tracking the Cardinal Points
My first proper job after university was as a technician then research assistant at Oxford University studying these phenomena. I say ‘proper’ because when I left University, I became an itinerant archaeologist. This led me to digs in Switzerland, Northampton, East Anglia and Nottingham. Then, I got the job at the Research Laboratory for Archaeology and the History of Art, at Keble College, Oxford.
I worked for Dr. Mike Barbetti who was an expert on the wanderings of the Magnetic Pole. His interest was firstly in the pure science of the subject. But he was keen to explore the applied uses in Archaeology as well. So, after being appointed as a Research Fellow at Oxford, he set up an epic journey from his native Australia to Oxford. It went via some of the iconic sites of Palaeolithic Archaeology, including Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. The site of excavations by Mary and Louis Leakey.
To plot the movements of the magnetic north, scientists needed dated samples. Early human sites provided dated sites over a long time span. Also, archaeomagnetism, as the discipline became known, offered the possibility of dating sites. Another application was to determine whether deposits were fired or not. One of the sites Mike sampled was a candidate for the first evidence of fire in human existence.
Cutting up Samples
As I said, Mike’s interest was discovering how the magnetic field of the earth changed over time. And, more importantly, what was the mechanism. He shipped back to Oxford samples of soil cast in Plaster of Paris. My job was to cut the samples up. I cut them up with an electric saw in a shed in the backyard of the Laboratory. Then we measured the direction and intensity of the magnetic field in the samples.
Soil contains particles of iron, and they align randomly. So a sample of soil has a low magnetic intensity and a random direction of magnetic field. But once heated up, the iron particles align to the current direction of the magnetic pole. Its intensity is proportional to the intensity of the Earth’s magnetic field. These measurements provide a method of plotting the changes of the magnetic field over time. And from these data, models can be constructed explaining how the iron in the earth’s core worked as a giant magnet.
Once we had built a reference curve for the movements and intensity of the magnetic pole over time, we hoped to develop another dating method. Other methods such as radio carbon, thermoluminescence, and tree ring dating, were being developed at the Research Laboratory in Oxford.
My part in Digital Heritage Part 1
Having got the results, I took them to the Oxford University Computer Centre. There, I typed them up onto machine-readable cards. Added a copy on cards of our computer programme written in Fortran, and gave them to the Computing Staff. The program and data were run through the Centre’s mainframe computer. (probably an IBM or ICL computer, the size of a house!). 24 hours later, I received a print-out to proofread.
I located mistakes, ran an editing run of punched cards, essentially instructing the computer: ‘on card two replace 2.5 with 2.6, and run the programme again’. I would pick up the results 24 hours later. It seems extraordinarily primitive now, but then it was an enormous saving of time.
And that, patient reader, was my early contribution to Digital Heritage and pure science. Mike published many articles of which I was joint author of three articles, two in the prestigious Science Journal Nature. And it is annoying that my citations in the groves of academia are still dominated by articles I co-wrote in the late 1970s/80s!
Mike’s work was important in the development of the study of the earth’s magnetic field. However, the use of archaeomagnetism has never risen above strictly limited. Occasionally, in specific circumstances, it can be useful. But those circumstances tend to be times when no other methods have worked. Most often, it is used in attempting to date kilns.
These are the papers:
Barbetti. M and K. Flude, ‘Palaeomagnetic Field Strengths from Sediments baked by Lava flows of the Chaine des Puys, France.’ Nature, Vol. 278 No 5700. 1979
Barbetti M., Y. Taborin, B. Schmider and K. Flude ‘Archaeomagnetic Results from Late Pleistocene Hearths at Etoilles and Marsangy, France’. Archaeometry 22. 1980
More on my contribution to Digital Heritage in posts to come.
OnThis Day
Duel Day is celebrated when the Duke of Wellington fought a duel against George Finch-Hatton, 10th Earl of Winchilsea, because of disagreement about Roman Catholic Emancipation. The duel was in Battersea Fields on 21 March 1829
First written March 2023, revised 21st March 2024



















![Chad is the patron saint of medicinal springs,[37] although other listings[38] do not mention this patronage.
St. Chad's Day (2 March) is traditionally considered the most propitious day to sow broad beans in England.](https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/haggerston_may_2020.jpg)