So, the old Sun is dying, and if the Sun keeps going down we are all going to die. To keep our anxiety to a minimum with all of nature seeming to be dying or hibernating, evergreens are a symbol of a promise/proof that life will continue through the dark days. So, with its bright-green leaves and its luminous berries, Holly is the ideal evergreen for the Solstice. And as the prickles symbolise Christ’s Crown of Thorns, and the berries the red blood of Jesus, the symbolism works, too, for Christians.
‘Ivy’ says Culpeper in his Herbal of 1653, says its winter-ripening berries are useful to drink before you ‘set to drink hard’ because it will ‘preserve from drunkenness’. And, moreover, the leaves (bruised and boiled) and dropped into the same wine you had a ‘surfeit’ of the night before provides the ‘speediest cure’. (The Perpetual Almanac of Charles Kightly)
Henry Mayhew (editor of Punch) in his ‘London Labour and London Poor’ (1851–62) talks of Christmasing for Laurel, Ivy, Holly, and Mistletoe. He calculated that 250,000 branches of Holly were purchased from street coster mongers every Christmas. He says that every housekeeper will expend something from 2d to 1s 6d, while the poor buy a pennyworth or halfpennyworth each. He says that every room will have the cheery decoration of holly. St Pauls Cathedral would take 50 to a 100 shillings worth.
He also calculates that 100,000 plum puddings are eaten. Mistletoe he believes is less often used than it used to be, and he hopes that ‘No Popery’ campaigners will not attack Christmassing again.

from the Gentle Author Spitalfields Life website
Culpeper on Ivy (1814 edition):
It is so well known to every child almost, to grow in woods upon the trees, and upon the stone walls of churches, houses, &c. and sometimes to grow alone of itself, though but seldom.
Time. It flowers not until July, and the berries are not ripe until Christmas, when they have felt Winter frosts.
Government and virtues. It is under the dominion of Saturn. A pugil of the flowers, which may be about a dram, (saith Dioscorides) drank twice a day in red wine, helps the lask, and bloody flux. It is an enemy to the nerves and sinews, being much taken inwardly, out very helpful to them, being outwardly applied. Pliny saith, the yellow berries are good against the jaundice; and taken before one be set to drink hard, preserves from drunkenness, and helps those that spit blood; and that the white berries being taken inwardly, or applied outwardly, kills the worms in the belly. The berries are a singular remedy to prevent the plague, as also to free them from it that have got it, by drinking the berries thereof made into a powder, for two or three days together. They being taken in wine, do certainly help to break the stone, provoke urine, and women’s courses. The fresh leaves of Ivy, boiled in vinegar, and applied warm to the sides of those that are troubled with the spleen, ache, or stitch in the sides, do give much ease. The same applied with some Rosewater, and oil of Roses, to the temples and forehead, eases the head-ache, though it be of long continuance. The fresh leaves boiled in wine, and old filthy ulcers hard to be cured washed therewith, do wonderfully help to cleanse them. It also quickly heals green wounds, and is effectual to heal all burnings and scaldings, and all kinds of exulcerations coming thereby, or by salt phlegm or humours in other parts of the body. The juice of the berries or leaves snuffed up into the nose, purges the head and brain of thin rheum that makes defluxions into the eyes and nose, and curing the ulcers and stench therein; the same dropped into the ears helps the old and running sores of them; those that are troubled with the spleen shall find much ease by continual drinking out of a cup made of Ivy, so as the drink may stand some small time therein before it be drank. Cato saith, That wine put into such a cup, will soak through it, by reason of the antipathy that is between them.
There seems to be a very great antipathy between wine and Ivy; for if one hath got a surfeit by drinking of wine, his speediest cure is to drink a draught of the same wine wherein a handful of Ivy leaves, being first bruised, have been boiled.
Happy Eponalia
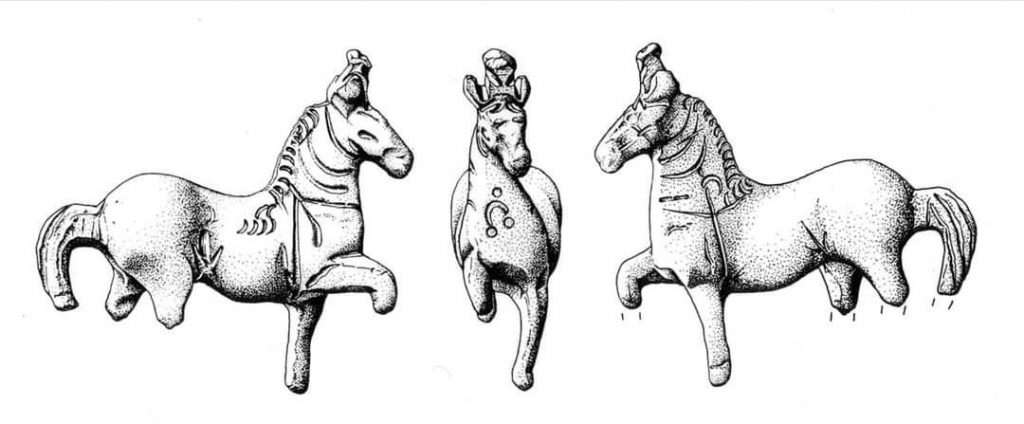
In 2021 I posted about Eponalia for the 18th Dec but I have now added it here and this is what I said:
I’ve been too busy working on my Jane Austen and Christmas Virtual Tour (I have just done that again this year) to post over the last few days. And I have, therefore, shamelessly stolen this post off my Facebook friend Sue Walker, who is a talented archaeological illustrator, artist and a very good photographer.
She wrote: ‘the 18th December is the festival of the Celtic goddess Epona, the protector of horses, she was adopted by the Romans and became a favourite with the cavalry. This finely sculpted bronze horse with a head dress and symbol on its chest is 37mm high – found in Bunwell #Norfolk #Archaeology’
https://www.complete-herbal.com/culpepper/ivy.htm
First published on December 17th 2022, Revised and republished December 2023