Vesta and the Vestal Virgins
For March 6th, Ovid in his Almanac Poem called ‘Fasti’ (Book III: March 6) tells the story of Vesta. She is Hestria, in Greece and is depicted on the Parthenon Marbles, standing near Zeus and Athene. She was the Goddess of the Hearth, of the fire that keeps families warm, and fed. Vesta had 6 Virgins as her Priestesses,. They had to remain 30 years, from before puberty, as a virgin, or they were buried alive. Any partners in sin were beaten to death. At the end of their term they could marry, retire, or renew their vows. That suggests they would be late 30s, early 40s before they could retire.
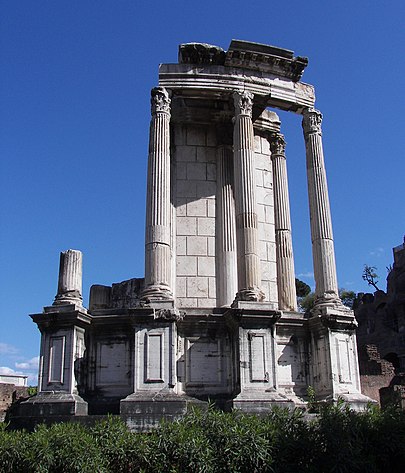
The Vestal Virgins tended Vesta’s hearth. It was not supposed to go out, as it had, in theory, come from Troy with Aeneas. Vesta’s Temple also housed the Palladium. This was a wooden status of Pallas Athene, that kept Troy, then Rome free from invasion. Odysseus and Diomedes had stolen it just before the Trojan Horse episode ended the 10-year-long Trojan War. (To read more about this, look at my post here.)
The Temple of Vesta was in Rome’s Forum, and it was a circular temple or a Tholos. Next to the Sacred Shrine at Bath was a circular Tholos, which may have been dedicated also to Vesta.

Here is what Ovid says in his March 6th entry:
When the sixth sun climbs Olympus’ slopes from ocean,
And takes his way through the sky behind winged horses,
All you who worship at the shrine of chaste Vesta,
Give thanks to her, and offer incense on the Trojan hearth.
To the countless titles Caesar chose to earn,
The honour of the High Priesthood was added.
Caesar’s eternal godhead protects the eternal fire,
You may see the pledges of empire conjoined.
Gods of ancient Troy, worthiest prize for that Aeneas
Who carried you, your burden saving him from the enemy,
A priest of Aeneas’ line touches your divine kindred:
Vesta in turn guard the life of your kin!
You fires, burn on, nursed by his sacred hand:
Live undying, our leader, and your flames, I pray.
Translated by A. S. Kline online here.
Caesar is Julius Caesar. Aeneas was the last Trojan who survived the end of Troy. He came to Italy, founded a Kingdom (Latium) in which his descendant, Romulus, would found Rome. This is told in Virgil’s Aeneid.
Rhea Silvia the Vestal Virgin
At the beginning of Book 3 of Fasti. Ovid tells us the story of Rome’s foundation, and how Mars took Silvia the Vestal while she slept. She was descended from Aeneas. She later gave birth to Romulus and Remus. The Goddess Vesta was displeased and put the holy fires out, shook the altar and shut the eyes of her image. Venus was more forgiving. The children survived. But Silvia eventually drowned in the Tiber.
Foundation Calendars
The new City chose Mars, the Roman God of War, father of their founder – as its patron God. He suited the Romans with their destiny to rule the world. So March was named after Mars, and 1st March was the beginning of the Roman year. (At least in Rome’s early days as I discussed in my post on March 1st). Ovid in the ‘Fasti’ makes the point, through Romulus’s voice and explains something about the various Calendars run by different tribes/Cities:
‘And the founder of the eternal City said:
‘Arbiter of War, from whose blood I am thought to spring,
(And to confirm that belief I shall give many proofs),
I name the first month of the Roman year after you:
The first month shall be called by my father’s name.’
The promise was kept: he called the month after his father.
This piety is said to have pleased the god.
And earlier, Mars was worshipped above all the gods:
A warlike people gave him their enthusiasm.
Athens worshipped Pallas: Minoan Crete, Diana:
Hypsipyleís island of Lemnos worshipped Vulcan:
Juno was worshipped by Sparta and Pelopsí Mycenae,
Pine-crowned Faunus by Maenalian Arcadia:
Mars, who directs the sword, was revered by Latium:
Arms gave a fierce people possessions and glory.
If you have time examine various calendars.
And you’ll find a month there named after Mars.
It was third in the Alban, fifth in the Faliscan calendar,
Sixth among your people, Hernican lands.
The position’s the same in the Arician and Alban,
And Tusculum’s whose walls Telegonus made.
It’s fifth among the Laurentes, tenth for the tough
Aequians,
First after the third the folk of Cures place it,
And the Pelignian soldiers agree with their Sabine
Ancestors: both make him the god of the fourth month.
In order to take precedence over all these, at least,
Romulus gave the first month to the father of his race.
Nor did the ancients have as many Kalends as us:
Their year was shorter than ours by two months.
The Sabine Women
This section mentions the Sabines, these were a neighbouring tribe. The Romans were short of women, so they kidnapped the Sabine Women. It became known as the Rape of the Sabine Women. People argue whether they were raped or kidnapped. Romulus worked to convince the women that it was done out of necessity for Rome’s future. The Women, or some of them, certainly tried to escape. Many became pregnant. The Sabine Army approached and entered Rome determined to free their women and enact revenge on their neighbours. Ovid tells the story of Hersilia, Romulus’s wife trying to persuade the Women. The poem then returns to Mars’ viewpoint, and ends with a beautiful description of spring in March.
The battle prepares, but choose which side you will pray
for:
Your husbands on this side, your fathers are on that.
The question is whether you choose to be widows or
fatherless:
I will give you dutiful and bold advice.
She gave counsel: they obeyed and loosened their hair,
And clothed their bodies in gloomy funeral dress.
The ranks already stood to arms, preparing to die,
The trumpets were about to sound the battle signal,
When the ravished women stood between husband and
father,
Holding their infants, dear pledges of love, to their breasts.
When, with streaming hair, they reached the centre of the
field,
They knelt on the ground, their grandchildren, as if they
understood,
With sweet cries, stretching out their little arms to their
grandfathers:
Those who could, called to their grandfather, seen for the
first time,
And those who could barely speak yet, were encouraged
to try.
The arms and passions of the warriors fall: dropping their
swords
Fathers and sons-in-law grasp each other’s hands,
They embrace the women, praising them, and the
grandfather
Bears his grandchild on his shield: a sweeter use for it.
Hence the Sabine mothers acquired the duty, no light one,
To celebrate the first day, my Kalends.
Either because they ended that war, by their tears,
In boldly facing the naked blades,
Or because Ilia happily became a mother through me,
Mothers justly observe the rites on my day.
Then winter, coated in frost, at last withdraws,
And the snows vanish, melted by warm suns:
Leaves, once lost to the cold, appear on the trees,
And the moist bud swells in the tender shoot:
And fertile grasses, long concealed, find out
Hidden paths to lift themselves to the air.
Now the field’s fruitful, now ís the time for cattle breeding,
Now the bird on the bough prepares a nest and home:
It’s right that Roman mothers observe that fruitful season,
Since in childbirth they both struggle and pray.
Add that, where the Roman king kept watch,
On the hill that now has the name of Esquiline,
A temple was founded, as I recall, on this day,
By the Roman women in honour of Juno.
But why do I linger, and burden your thoughts with
reasons?
The answer you seek is plainly before your eyes.
My mother, Juno, loves brides: crowds of mothers
worship me:
Such a virtuous reason above all befits her and me.í
Bring the goddess flowers: the goddess loves flowering
plants:
Garland your heads with fresh flowers,
Ovid Fasti translated by A. S. Kline online here.
Seven Brides for ‘Seven Brothers
My children’s favourite film in childhood was Seven Brides for ‘Seven Brothers’. It was loosely based on the Rape of the Sabine Women.

First published in 2024, republished in 2025.



