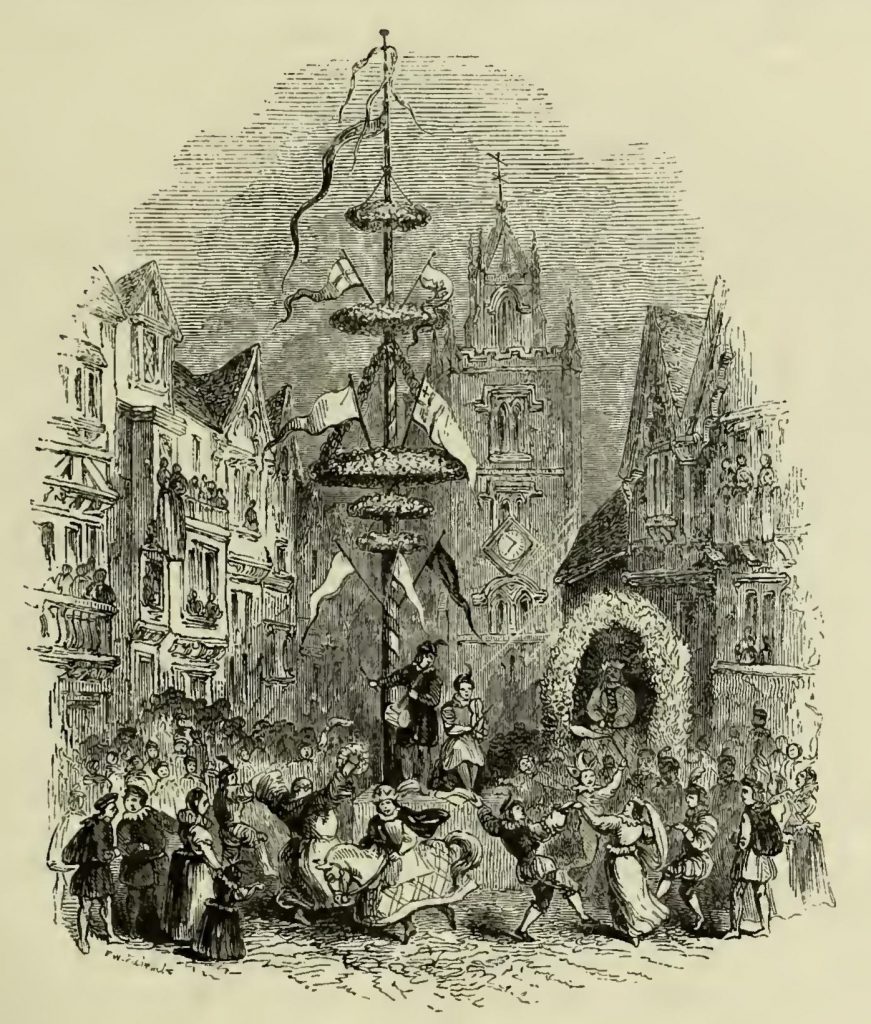
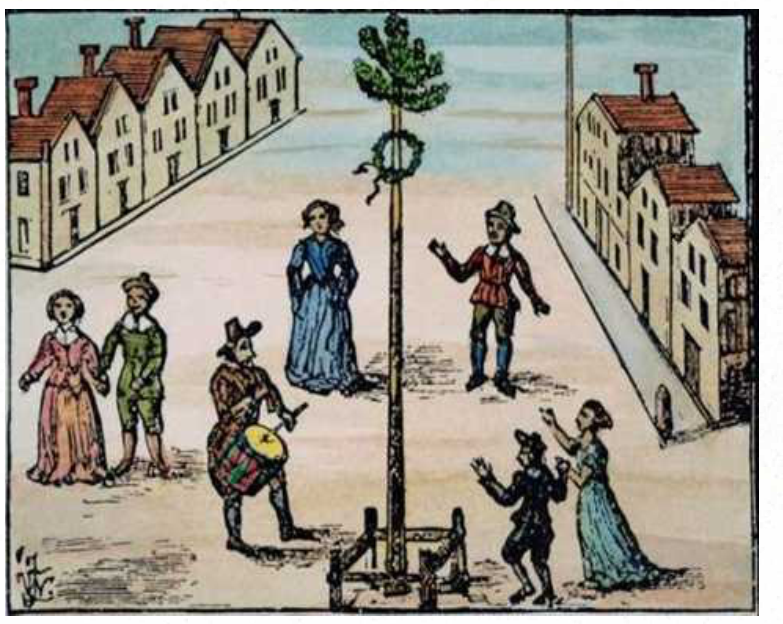
Philip Stubbes, in his Anatomy of Abuses of 1583, fired a broadside at the tradition of dancing around the Maypole when he wrote a vitriolic attack on pagan practices. He said they had ‘as Superintendent and Lord ouer their pastimes and sportes: namely, Sathan Prince of Hell’ as they erected ‘this stinking Idoll’. Stubbes suggested that of the maids that went out to the woods on May Eve less than one-third returned ‘undefiled’.
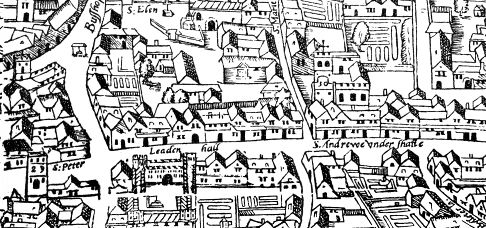
The Maypole was stored at St Andrew Cornhill, which became known as St Andrew Undershaft. In 1517, it was attacked during the ‘Evil May Day riot’, which the Recorder of the time, Thomas More, helped quell. (300 were arrested and one hanged). The shaft was returned to its place under the eves of the houses in Shaft Alley, but apparently banned from being raised.
But in 1549, the curate of nearby St Katharine Cree Church made an inflammatory speech which led to a Puritan mob cutting the shaft into pieces and burning it. I always imagine the Curate’s sermons to be along the same lines as Phillip Stubbes attack on the Maypole:
‘But their chiefest iewel they bring from thence is the Maie-poale,
which they bring home with great veneration, as thus: They haue
twentie, or fourtie yoake of Oxen, euery Oxe hauing a sweete
Nosegaie of flowers tyed on the tip of his homes, and these Oxen
drawe home this Maie-poale (this stinking ldoll rather) which is
couered all ouer with Flowers and Hearbes, bound round about
with strings from the top to the bottome, and sometimes painted
with variable collours, with two or three hundred men, women and
children following it, with great deuotion. And thus being reared
vp, with handkerchiefes and flagges streaming on the top, they
strawe the ground round about, bind green boughes about it, set
vp Summer Haules, Bowers, and Arbours hard by it. And then fa!
they to banquet and feast, to leape and daunce about it, as the
a Heathen people did, at the dedication of their ldolles, whereof this
is a perfect patteme, or rather the thing it selfe. I haue heard it
crediblie reported (and that viua voce) by men of great grauity,
credite, and reputation, that of fourtie, threescore, or a hundred Maides,
going to the wood ouemight, there haue scarcely the third part of them returned home againe vndefiled.‘
Phillip Stubbes from ”A Critical Edition Of Philip Stubbes’s Anatomie Of Abuses‘ By Margaret Jane Kidnie.
The unraised pole seems to have survived until the beginning of the Civil War, (1644) when it was destroyed. But at the Restoration of Charles II a new and huge Maypole was joyously erected 134 ft high (41 metres) in the Strand. This was danced around till 1713 when it was replaced and the original sold to Isaac Newton who used it to support the biggest telescope in Europe which was erected in Wanstead by a friend.
And that, my friends, is how you get from Superstition to Science in one easy story.

Postscript. I have always said that the sermon that led to the destruction of the Shaft in 1549 was made at St Paul but cannot remember where I read this. The suggestion that the Maypole in Cornhill was not used after 1517 seems strange because why then would it rouse a crowd to riot in 1549? Of the sources I have at hand, the London Encyclopedia mentions the riot of 1517 in its entry on St Andrew Undershaft but doesn’t elaborate more. ‘Layers of London‘ says ‘It was last raised in 1517 when ensuing riots led to the celebration being banned.’ which is definitive sounding. But is it? I wonder if it was banned for a year or two, then allowed again, and finally stopped in 1549?
First written in 2023 and revised on May 2nd 2024.