Midsummer Solstice is the 21st of June, but the Celtic version of it began when the Celtic Day begun, on June 20th, which we would call Midsummer Eve. Midsummer is a fire festival, dedicated to the Celtic Fire God, Belinus. His name might mean Powerful One or Shining One, and he is linked to Apollo, one of the Greco-Roman Sun Gods. His main festival is Beltane, May Day, but many of the attributes of May celebrations and indeed Halloween celebrations are also carried out in Midsummer.
In the early medieval period, the Church hijacked Midsummer’s Day and transferred it to June 24th St John the Baptist’s Day. John was born 6 months before Jesus. John Aubrey in the 17th Century writes:
‘Still in many places on St John’s Night they make Fires on the Hills: but the Civil Warres coming on have putt all these Rites or customes quite out of fashion.’
John Aubrey, Miscellanies, 1695
Like May Fires, the fire should be made from wood donated from all farms in the area, and using a range of trees, ideally collected by 9 men and from 9 different trees. Blazing branches should be carried sunwise around the fields to bless the crops, and it was good luck to jump over the ashes of the fire.
To prepare for Midsummer remember that it is, like Halloween, a uncanny period when Hobgoblins, Fairies and Sprites, are, like in Shakespeare’s Play, Midsummer’s Night’s Dream, all abroad making mischief.
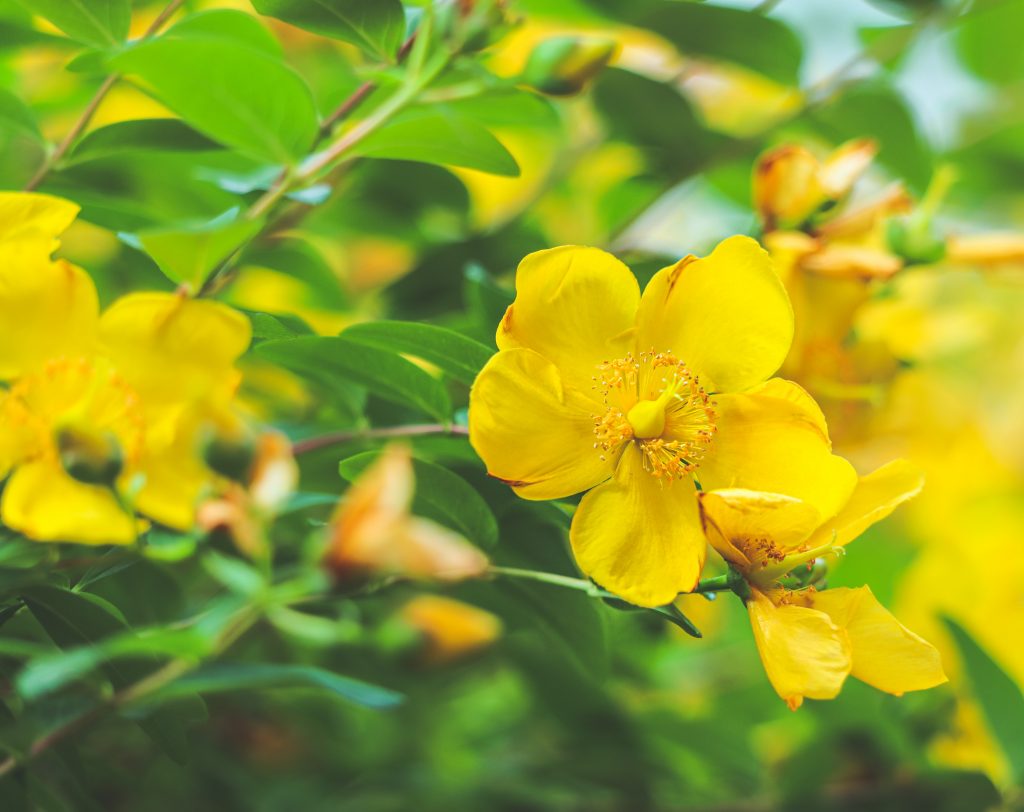
First in the line of defence against the infernal is St John’s Wort, known as Chasse-diable, Demon Chaser, Fuga Daemonum (amongst many other appellations) It was used to keep demons away, and to exorcise haunted houses. John Aubrey in ‘Miscellanies’ talks about a haunted London house which was cured by a Doctor who put St John’s Wort under the pillow of the bed at night. Bankes Herbel 1525 says:
‘The virtue of St John’s Wort is thus. If it be put in a man’s house, there shall come no wicked sprite therein.’
Vervain, yarrow, corn marigold, and orpins were also used often woven into garlands, and hung around the necks of cows, or on door lintels as protection. If the St John’s Wort withered, the picker was to die or at least endure disappointment. If orpins entwined themselves on Midsummer’s Night, marriage would follow.
A girl seeking love should walk around the Church seven or twelve times (accounts vary!) at midnight scattering hempseed, and singing:
Hempseed I sow
Hempseed I hoe
Let him that is my true love
Come after me and mow
In the South West of England, there was a custom to watch the church porch on Midsummer Evening, when the spirits of all the living people of the village could be seen entering the church. Those not seen coming out again would surely die, as would any watcher foolish enough to fall asleep.
Orpine, (Sedum Telephium) aka Live Long, or Life Everlasting was valued for the length of time it remained fresh after being gathered. Medicinally, it was considered good to use outwardly to cool scaldings, inflammations, and wounds.

St John’s Wort has a reputation for helping with depression, menopausal symptoms, ADHD, anxiety and other conditions.

Thanks to the ‘Customs and Ceremonies of Britain’ by Charles Kightly.
First written in June 2023, and revised and republished in June 2024