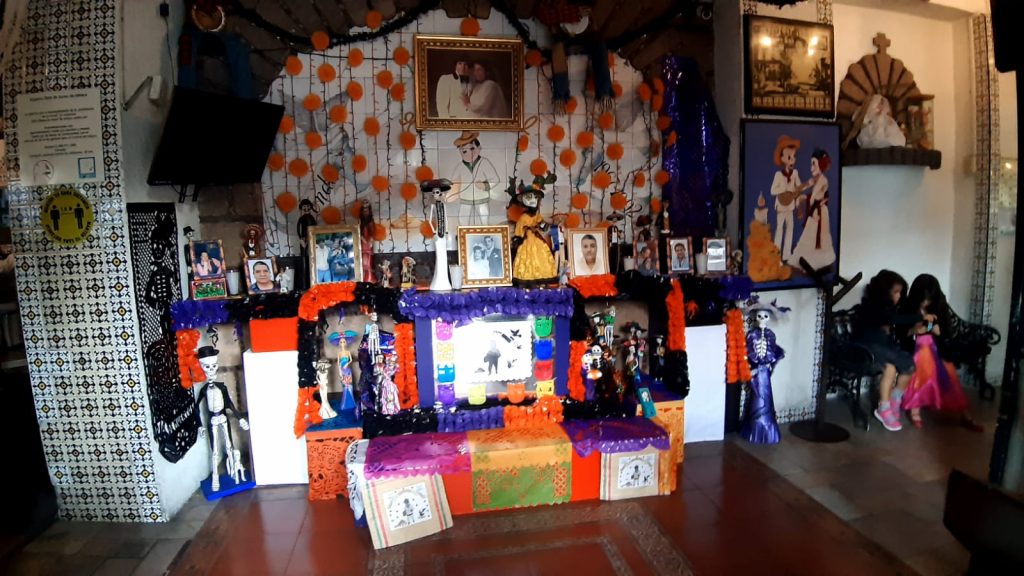
Mexican Day of the Dead, in fact, the second day of El Dia de Muertos. Here is a video from Mexico, which you will enjoy for its Latin song and images of the Day of the Dead in Mexico. (It’s on Facebook, so may not work unless you have a login).
Today is the day to celebrate all those loved ones who have passed away. To keep them in mind, to remind you still care about them. It is the third day of the season of Allhallowstide, following All Hallows Evening (Halloween), and All Saint’s Day.
Beata, who comes from Poland, tells me that, November the 1st is a happy day when relatives visit the cemeteries of the dead loved ones bringing chrysanthemums to decorate the graves. It’s a happy day for the dead because they are being remembered and visited by their loved ones. Today, November 2nd, is a more sombre day – a day to stay at home and think of the loved one’s perhaps looking through albums of photographs.
In England it was the time of year in which ‘Souling’ used to take place. Households made soul-cakes, children or people in need of food come to visit and are given soul cakes in exchange for praying for the dead.
Soul, soul, for a souling cake.
I pray good Missus for a souling cake.
Apple or pear, plum or cherry.
Anything good to make us merry.Traditional rhyme from Shropshire and Cheshire
This is based upon the idea of Purgatory, and the belief that intervention on Earth can influence the amount of time an ancestor spends in purgatory for their sins.
John Aubrey (1626 – 1697), antiquarian, collector of folklore and writer, mentions a custom in Hereford which shows a variant of the idea.
In the County of Hereford was an old Custom at Funerals, to hire poor people, who were to take upon them all the Sins of the part deceased. One of them I remember (he was a long, lean, lamentable poor rascal). The manner was that when a Corpse was brought out of the house and laid on the Bier; a Loaf of bread was brought out and delivered to the Sin-eater over the corps, as also a Mazer-bowl full of beer, which he was to drink up, and sixpence in money, in consideration whereof he took upon him all the Sins of the Defunct, and freed him (or her) from Walking after they were dead.v
John Aubrey, Remains of Gentilism 1688

This belief in the power of action in the Here and Now to lubricate passage through Purgatory to the Ever After was a major part of fund-raising for Catholic Institutions before the Reformation. For example, in the records of St Thomas Hospital, Southwark, a wealthy widow called Alice (de Bregerake – if I remember the spelling correctly) left her wealth to the hospital in return for an annual Rose rent; lifetime accommodation in the Hospital in Southwark, and for the monks and nuns to pray for her soul and the souls of her ancestors.

Revised 2nd Nov 2023. First published 2nd Nov 2021